What Is the Google Display Network?
The Google Display Network (GDN) is a group of millions of websites, apps, and videos where Google ads can appear.
Here’s what a display ad can look like on the GDN:

Collectively, the GDN reaches a huge percentage of internet users worldwide.
You can use a type of Google ads called display ads to serve your ads on the Google Display Network. And reach millions of potential customers.
Why Use the GDN?
The Google Display Network offers immense reach for marketers.
Because it places ads on such a wide range of websites and platforms, the GDN can be an effective way to reach broad, diverse audiences.
You’ll reach people who aren’t necessarily looking for your products or services in search results.
Nearly every website and blog has content that relates to at least one of your target keywords.
And the GDN can serve ads to such websites and blogs.
It’s a great way to increase brand visibility and awareness. And drive sales.
How Does the Google Display Network Work?
The GDN can serve your online ads on sites, apps, or videos related to your business. And to users who match the specific criteria you define.
Let’s see how it works in more detail.
Audience Targeting Based on Interests
Interest targeting lets you show your ads to people interested in your products or services.
Or those who engage in activities related to your business.
You can choose from three main interest-targeting categories:
- Affinity Audiences
- Custom Affinity Audiences
- In-Market Audiences

Affinity Audiences
This category includes 80 different groups based on interests. Such as “running enthusiasts,” “action movie lovers,” or “book lovers.”
You can show your ads to one or more of these audiences.
There isn’t a limit to the number of affinities you can add. However, the more you add, the more targeted your audience and the smaller your reach (possible impressions).
Custom Affinity Audiences
You can narrow your targeting further by using search terms (called keywords) to create your custom audiences.
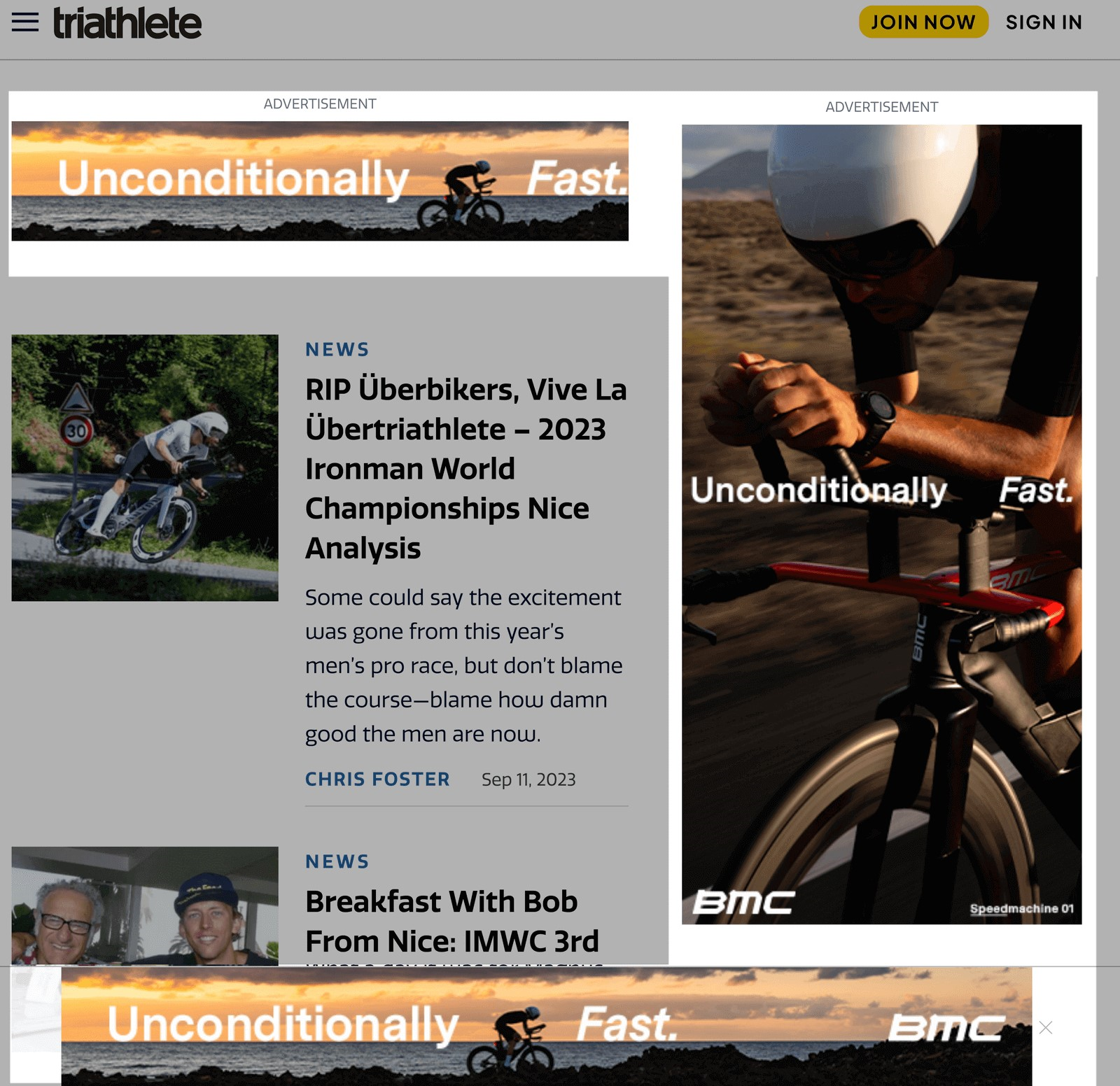
For example, if you’re running GDN ads for your triathlon gear store, you can use keywords like “triathlon training,” “beginner triathletes,” or “triathlon events.”
Google will show your ads to people visiting sites that contain those keywords.
You can even add specific URLs your audience might visit. And target sites where you’d like your ad to appear.
In this case, that could be triathlete.com or ironman.com.
Like this:
In-Market Audiences
This targeting category lets you find people actively looking at products or services similar to yours.
It’s useful if you’re looking to drive awareness among those “in-market” to buy. Aka people with high purchase intent.
Using the same example, these might be people who have added triathlon gear to their shopping cart on another website.
Or even those who’ve watched product review or comparison videos.
Audience Targeting Based on Demographics
Demographic targeting lets you reach potential customers who are of a certain age, gender, parental status, or household income.
And you can combine demographic targeting with interest targeting to reach a narrower, more relevant audience.
For example, let’s say you own a yoga studio for women. And you want to promote a special class for working mothers.
You can focus on the “Female” demographic group, within the “25-54” age range, and specify “Parent” status. Along with affinity groups based on yoga, pilates, and fitness.
Be mindful that the more specific your targeting, the fewer people will see your ads. Test several targeting combinations to see which brings you the most conversions.
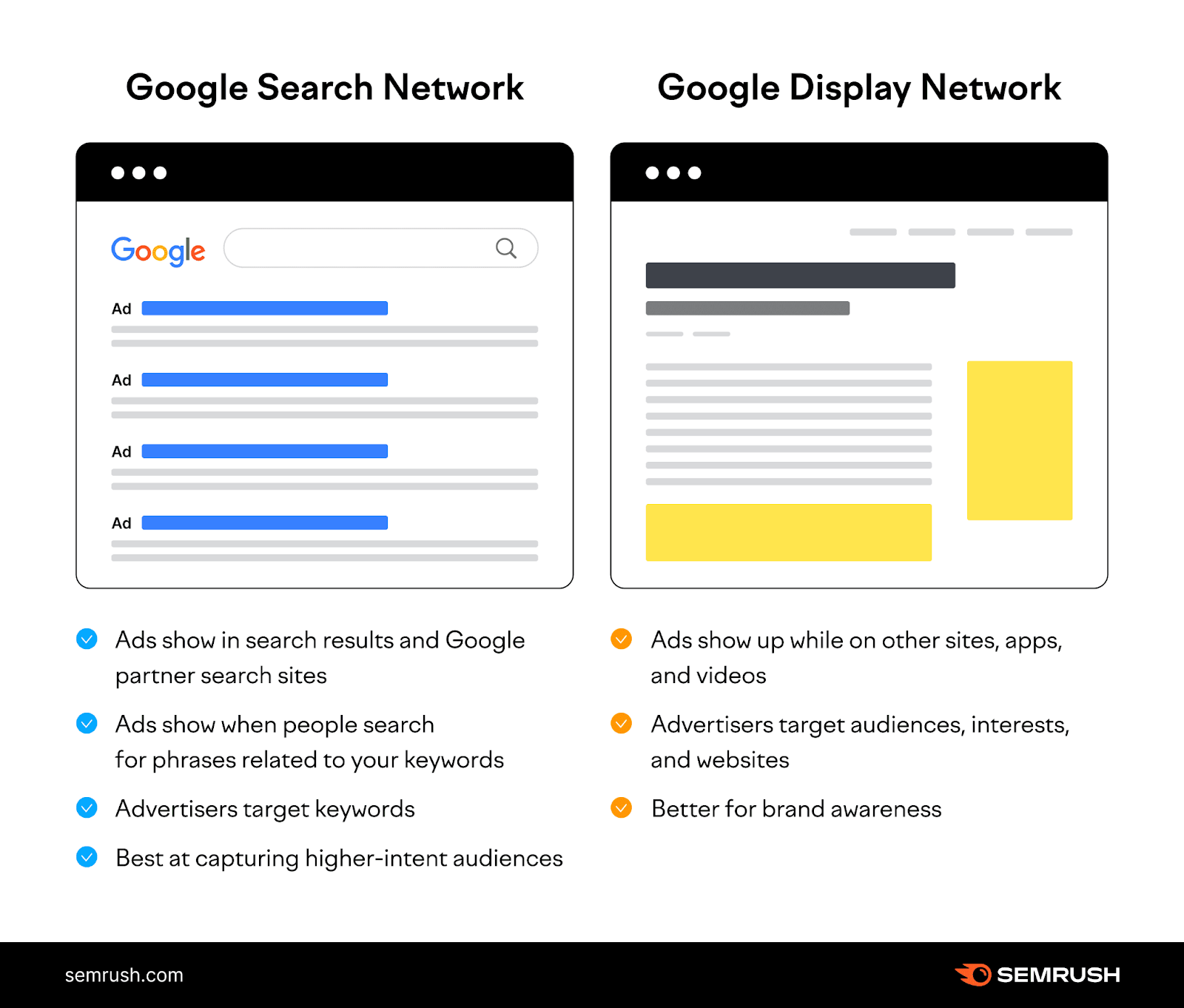
Google Display Network vs. Google Search Network
The main difference between the Google Display Network and the Google Search Network is where your ads show up.
The Google Search Network is a collection of websites and apps related to Google Search where your ads can appear.
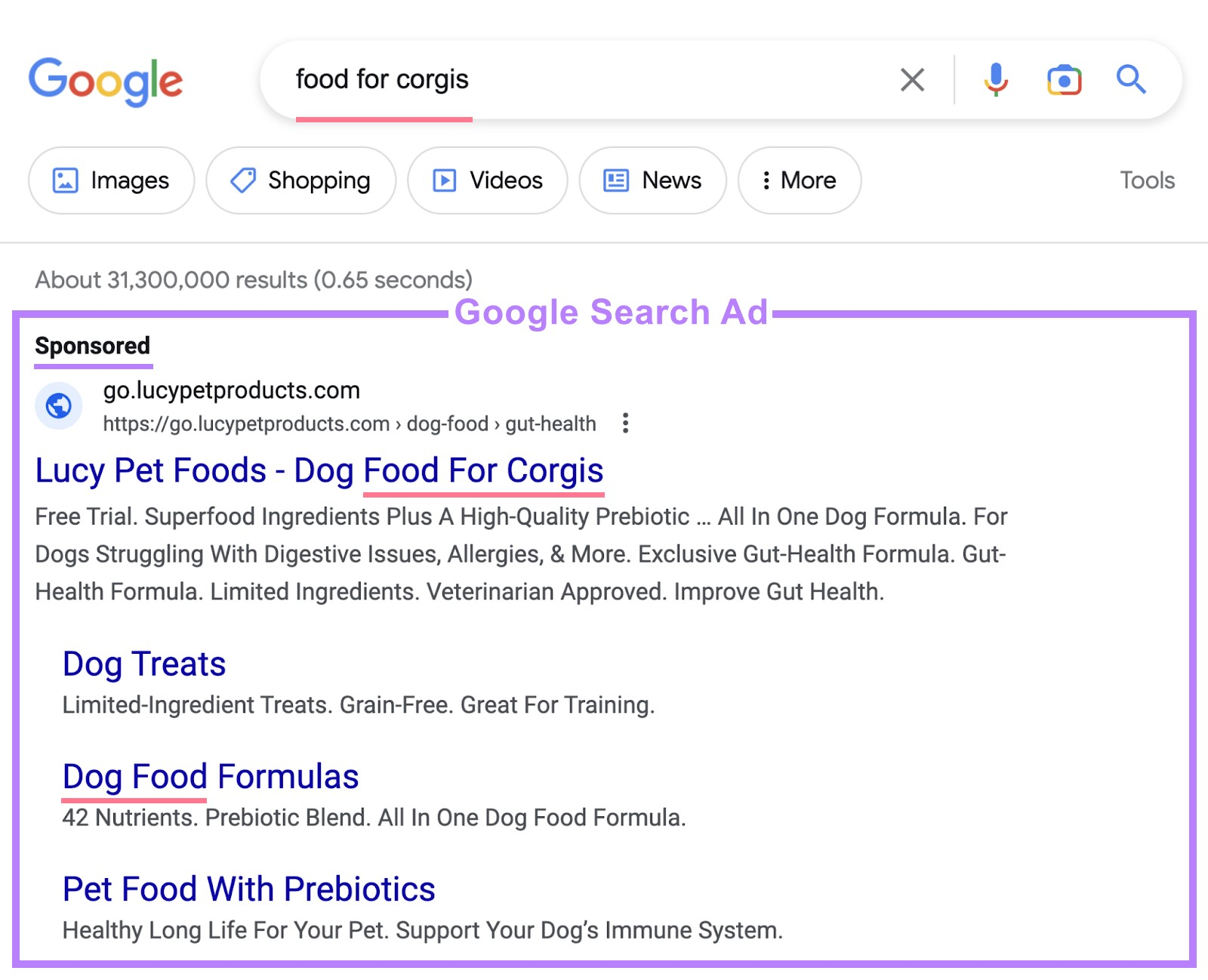
Your Google Search Network ads can show in Google search results and other Google partner search sites when people search for phrases related to your keywords.
Like this:
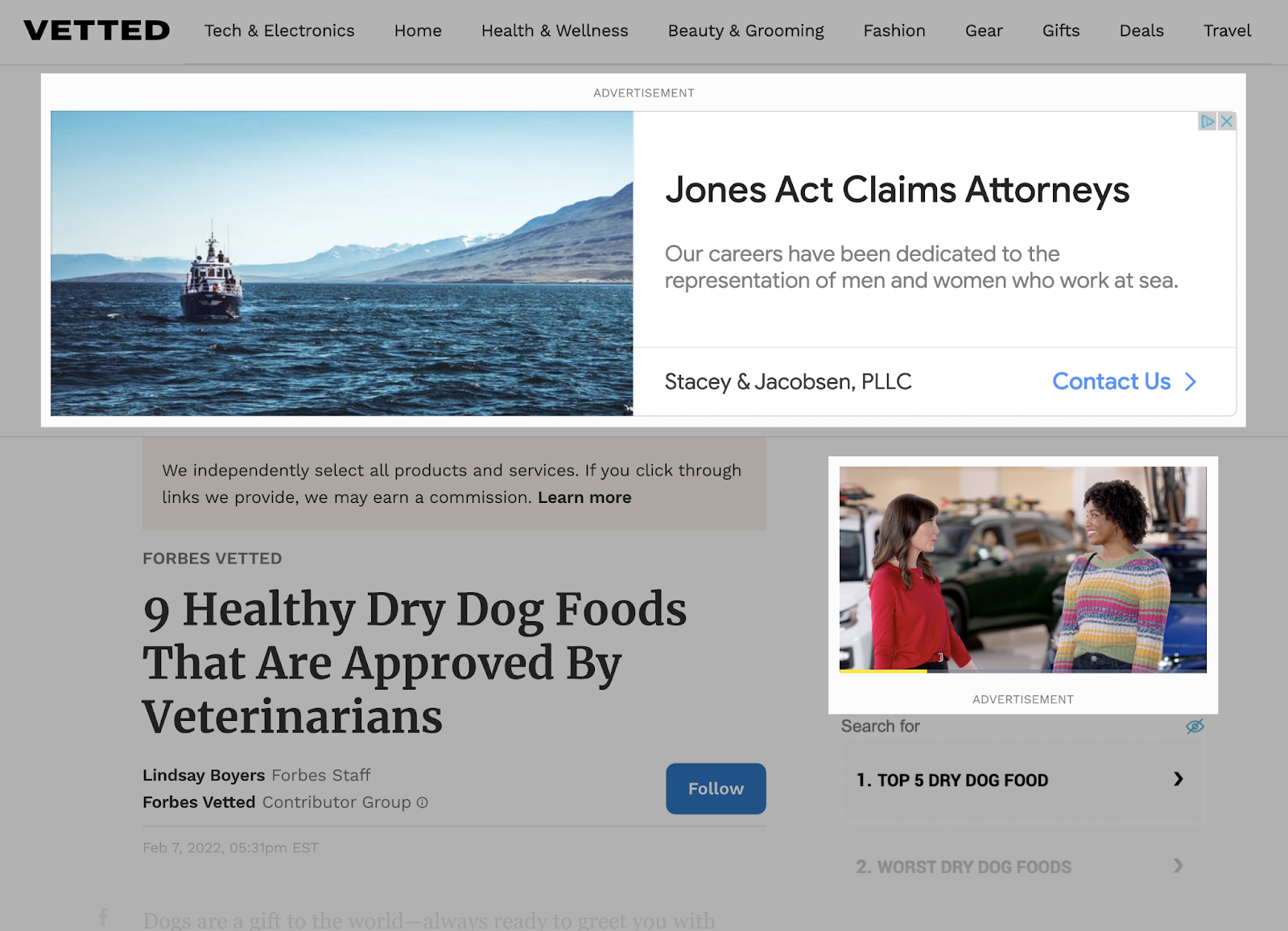
With the Google Ads Display Network, however, your ads show up while people are visiting other sites, apps, and videos.
You might not always reach folks actively searching for what you offer.
Like this:
There are other noticeable differences.
For example, with the Search Network, advertisers target keywords.
But in the Display Network, they target audiences, interests, and websites.
Plus, the Search Network tends to be best at capturing higher-intent audiences.
Whereas the Display Network is better for brand awareness.
Here’s a visual to illustrate the main differences between the two:
Further reading:
How Much Does It Cost to Use the Google Display Network?
The average cost per click on the Display Network is less than $1. But the total cost will ultimately depend on your budget.
The GDN runs on a live auction system like the Google Search Network. And charges you every time someone clicks on your ads.
The great thing about GDN is that there’s generally less competition for keyword bids.
So, you’re more likely to reach users interested in your products or services. And although the intent may not be as strong, you get more impressions.
Which is what advertisers often turn to GDN for: awareness.
Further reading:
How to Create Google Display Ads
To create a display campaign and run your ads on the Display Network, you’ll need to go through your Google Ads account.
In the left-hand menu, select “Campaigns” and hit the plus button. Then, click “New campaign.”
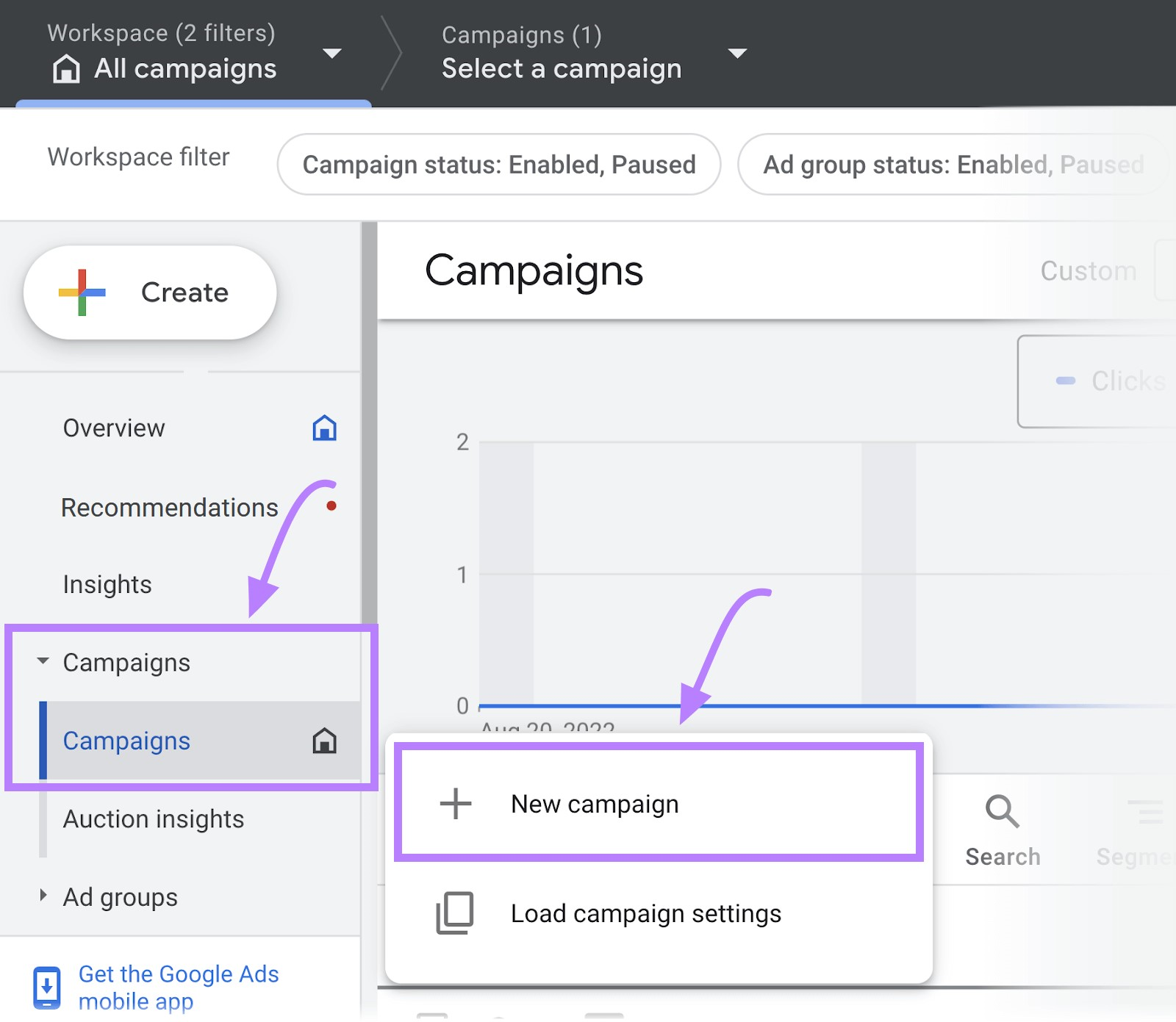
Next, choose your goal.
If you don’t have one yet, click “Create a campaign without a goal's guidance.”
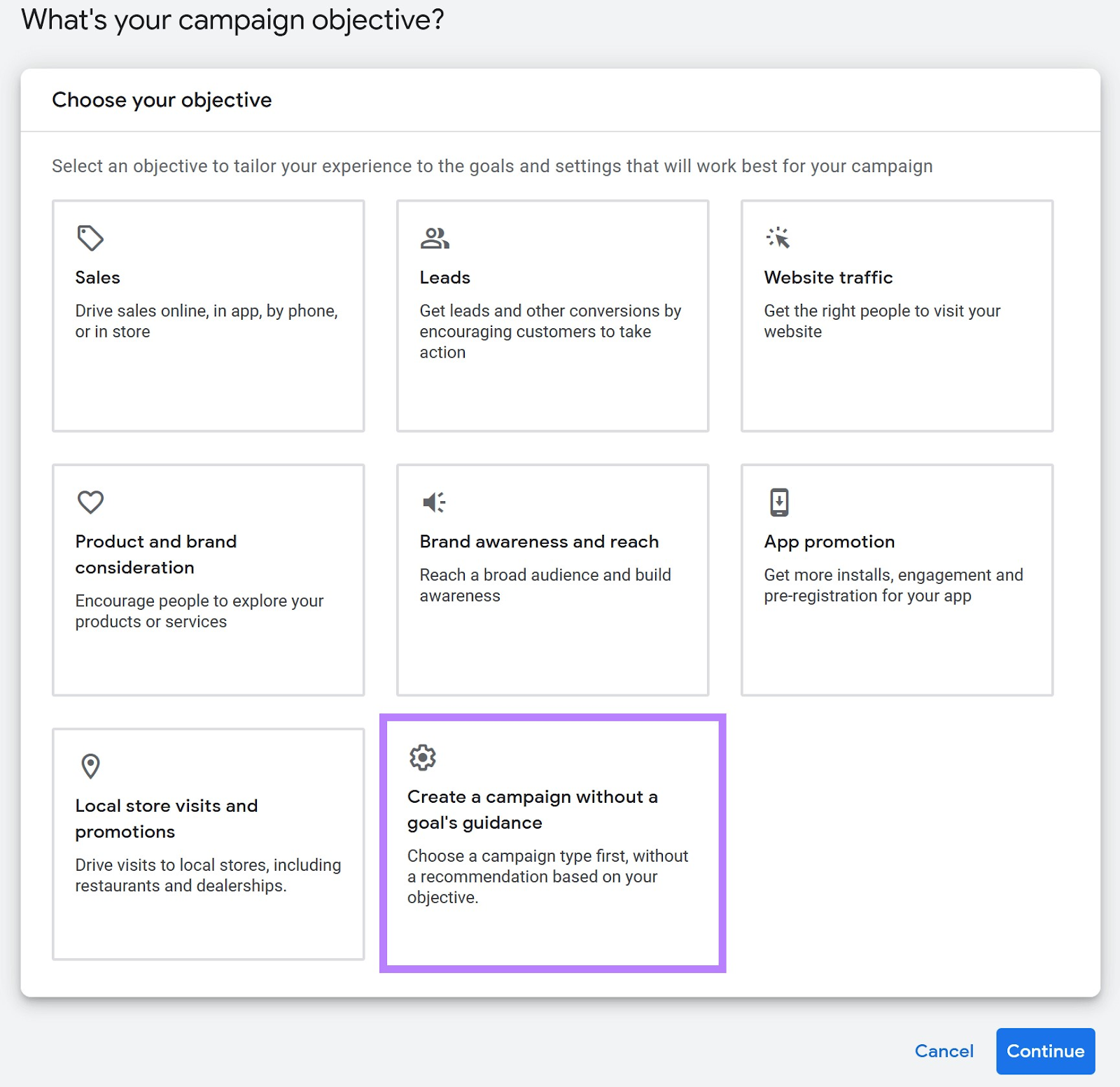
Then, select “Display” as the campaign type.
Now add your URL, enter a name for your campaign, and click “Continue.”
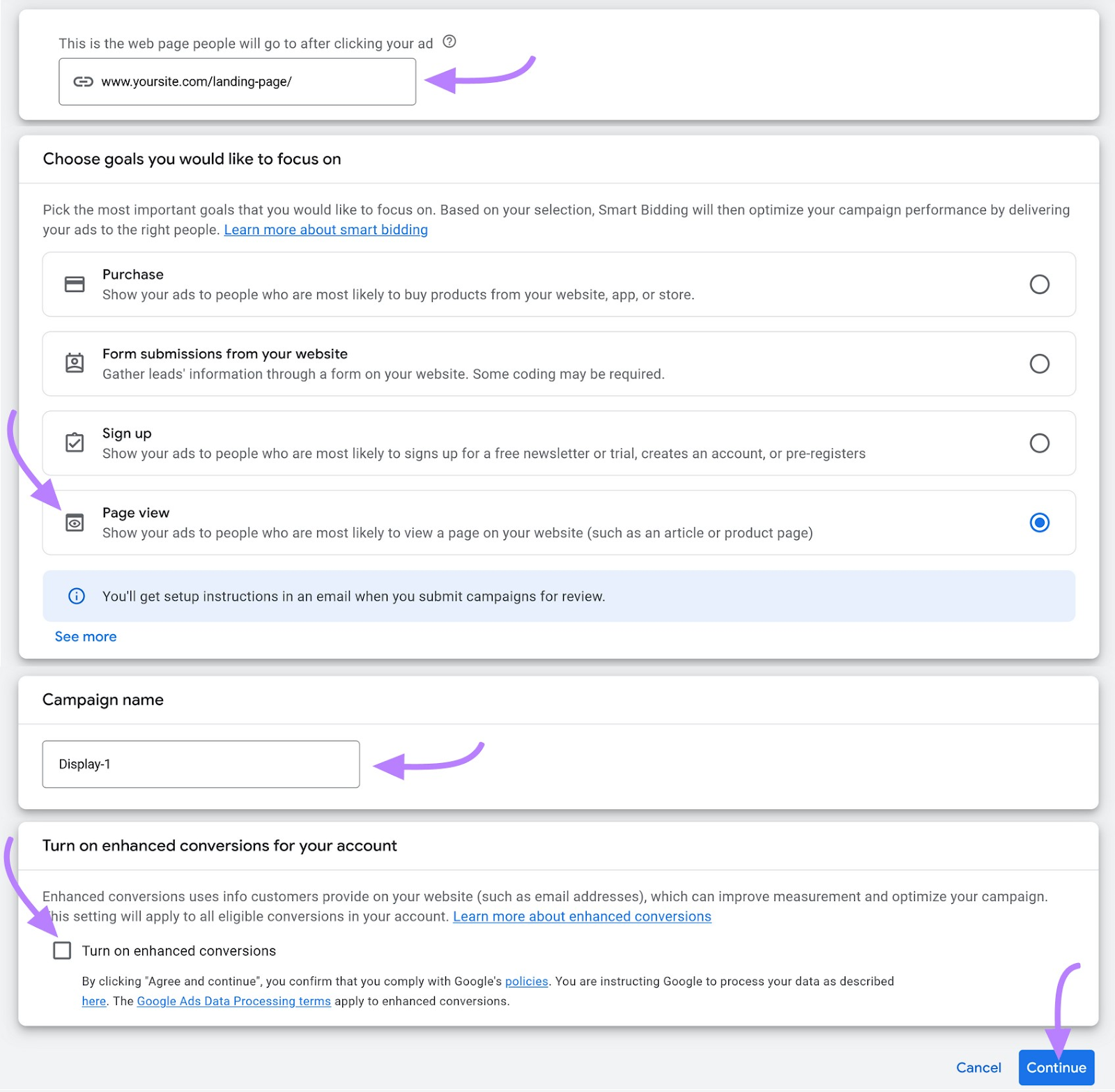
Then, you’ll be prompted to:
- Choose your location and language to target
- Set your budget and bidding strategy
- Add audience-targeting parameters
- Create ad copy and upload visuals
- Review and publish
Further reading:
- What Are Display Ads? Display Advertising Explained
- Google Keyword Planner: How to Use It to Find Keywords
How to Optimize Your Ads for the Google Display Network
Use the following guidelines to create optimized, responsive Display Network ads.
(Responsive display ads are the default ad type for GDN.)
Google will ask you to submit your assets (e.g., headlines, logos, images, and descriptions). And it’ll automatically adjust everything to fit different devices and available ad space.
Follow these best practices to create ads that reach users and drive performance:
Stick to Google’s Image Size Guidelines
Images are one of the most important elements of display ads. They help users understand your business, products, and brand.
And getting image sizing right is crucial for your ads to perform well.
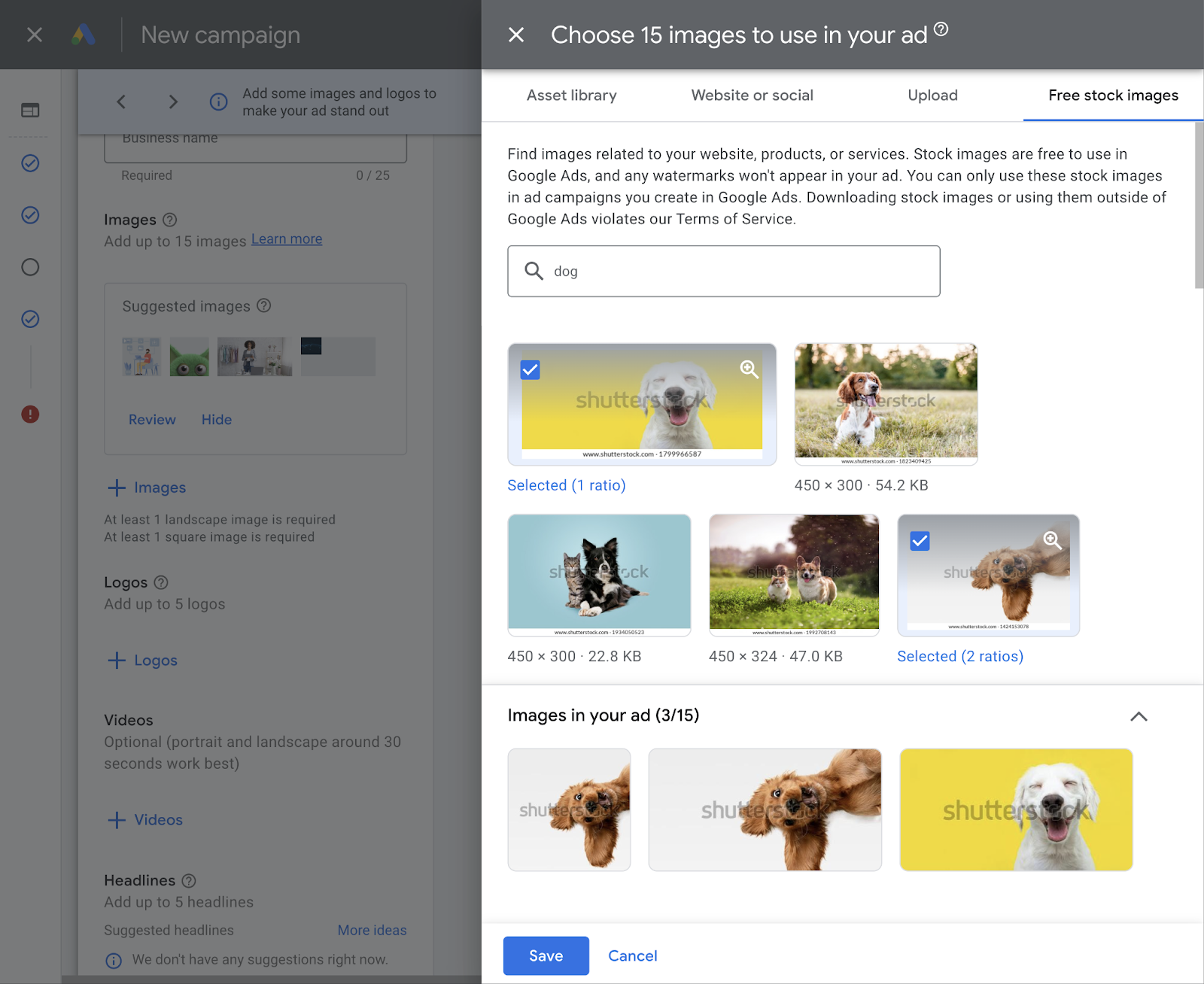
You can upload up to 15 images in three aspect ratios: square, landscape, and portrait. Or you can choose from Google’s free stock image library.
Like this:
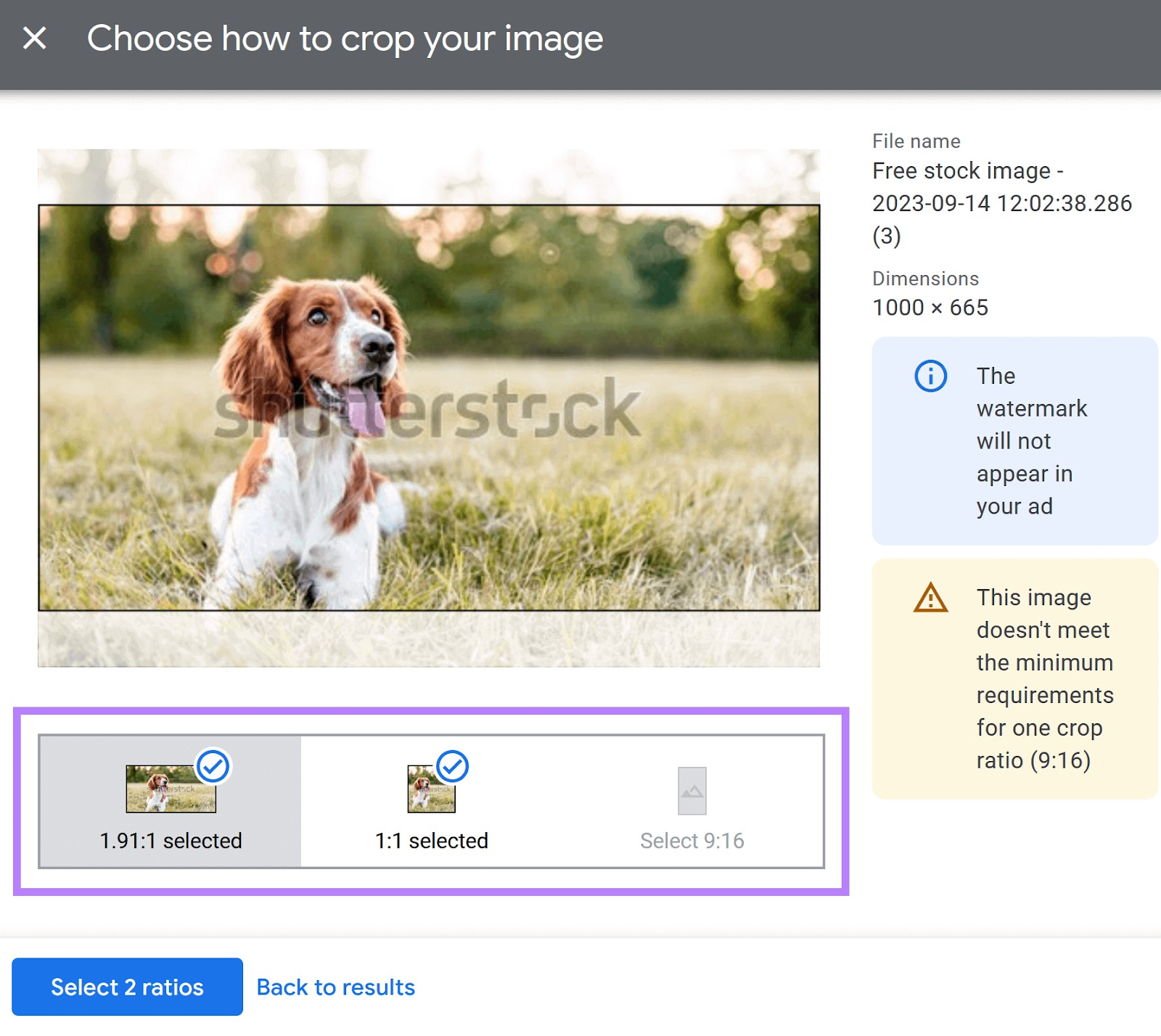
Google lets you set the ratio of the images you select from their library.
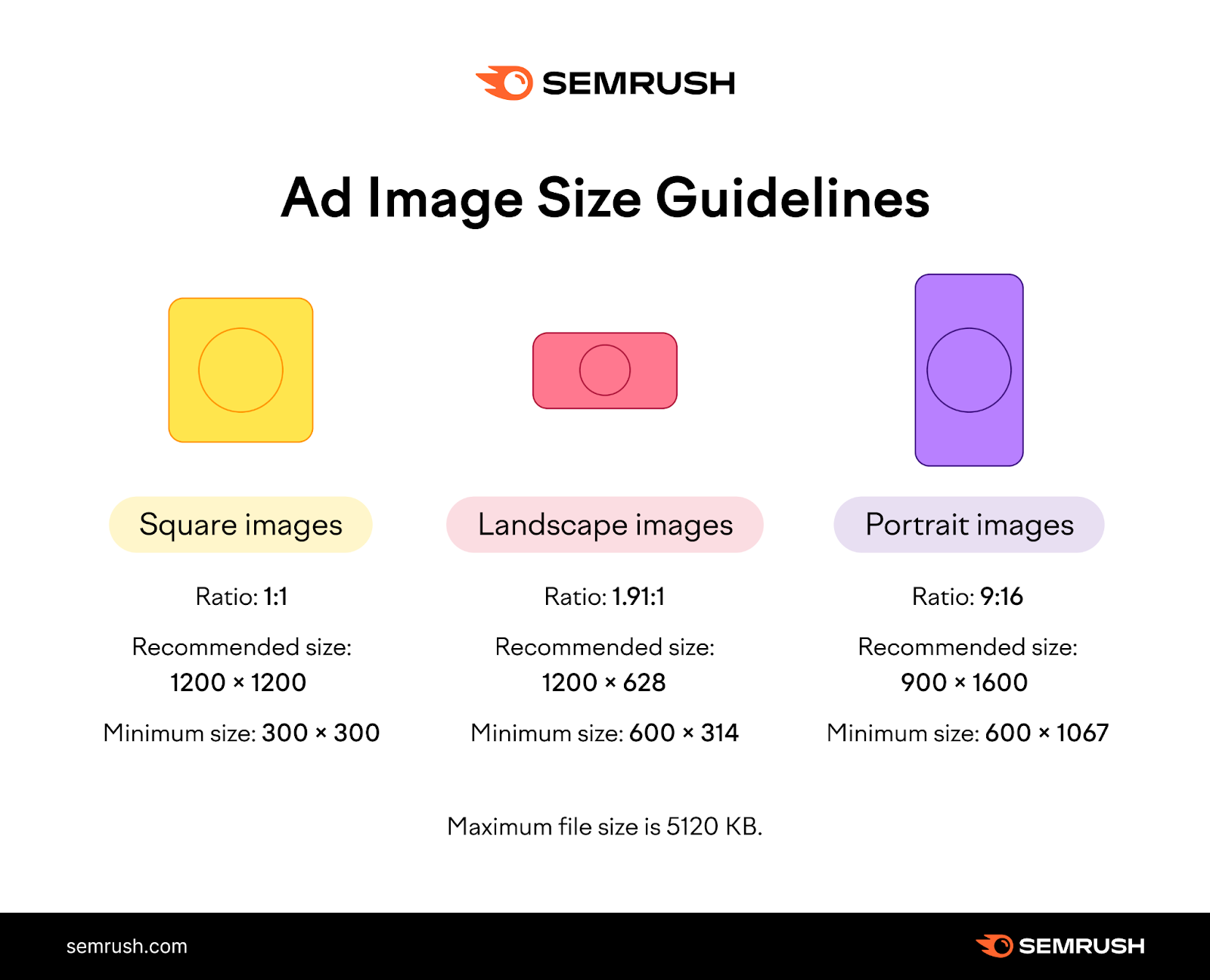
If you upload your images, follow these size guidelines:
Square images
Ratio: 1:1
Recommended size: 1200 x 1200
Minimum size: 300 x 300
Landscape images
Ratio: 1.91:1
Recommended size: 1200 x 628
Minimum size: 600 x 314
Portrait images
Ratio: 9:16
Recommended size: 900 x 1600
Minimum size: 600 x 1067
Make Sure Your Images Are High Quality
You want your images to be the right size, but you also want to ensure they’re high quality.
For best results, avoid images that are blurry, excessively filtered, upside-down, and outlined with a border.
Don’t:
- Overlay your logo on top of an image
- Overlay text or other graphics
- Overlay buttons
- Use logos with colorful backgrounds
Do:
- Use single images (no collages)
- Make your product or service the centerpiece
- Use physical settings with natural shadows and lighting
- Use logos with transparent or white backgrounds

Follow Google’s Text Recommendations
The most important guideline for your text is to use clear and simple language to describe your product or service.
And avoid generic text, all caps, and clickbait at all costs.
Short Headlines
You can add up to five short headlines in responsive display ads.
Don’t:
- Punctuate the end of short headlines
- Use the same copy in a headline and description
- Use your business’s name as the headline
- Use all caps
Do:
- Tell users what they can do: “Pay with a credit card”
- Spell out your offer: “Free next-day delivery”
- Make it unique and compelling: “Running shoes for less”

Keep all short headlines under 30 characters, or Google might cut them off. And make sure all your assets are unique.
Long Headlines
You can add one long headline for your responsive display ads.
Describe your brand’s or product’s value proposition in a compelling way. Make it useful and interesting.
Don’t:
- Punctuate the end of your long headline
- Repeat the copy from your short headlines
- Use all caps
- Use clickbait
Do:
- Write your headline so it can stand alone. Google may show it without description text.

Keep your long headline under 90 characters to avoid any cutoffs.
Descriptions
Google shows descriptions alongside short headlines. Not long headlines.
So, write your description copy to complement your short headlines.
You’re allowed to add up to five descriptions. Our recommendation? Add all five.
Don’t:
- Use generic messaging
- Use all caps
- Use clickbait
Do:
- Make text easy to read and understand
- Use sentence-case capitalization
- Use detail
- Clearly articulate the value proposition

Keep your descriptions under 90 characters to avoid cutoffs in certain layouts.
Understanding what the Google ad network is and how it works is only the first step.
If you want to see returns, you need to take things a step further.
That means looking at your competitors. Uncovering their ads, ad spend, and display network strategies.
And building on those insights.
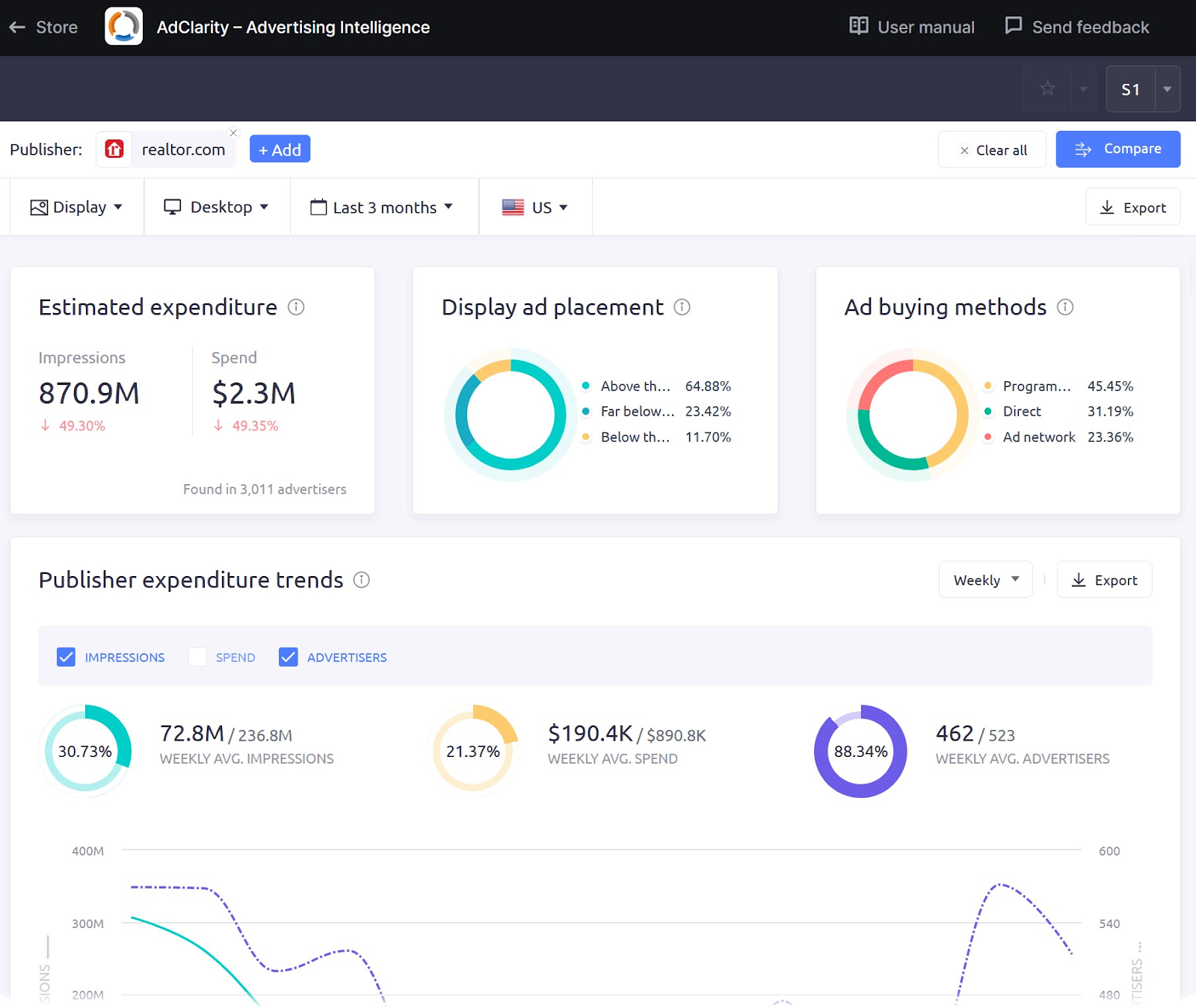
For example, a tool like AdClarity can help you:
- Analyze your competitors’ digital campaigns (in detail)
- Understand where (and how much) your competitors are spending on ads
- Compare (and benchmark) competitor strategies with your own
- See what the best-performing advertisers are doing
And more. From a database of 650,000 advertisers in 50-plus global markets.
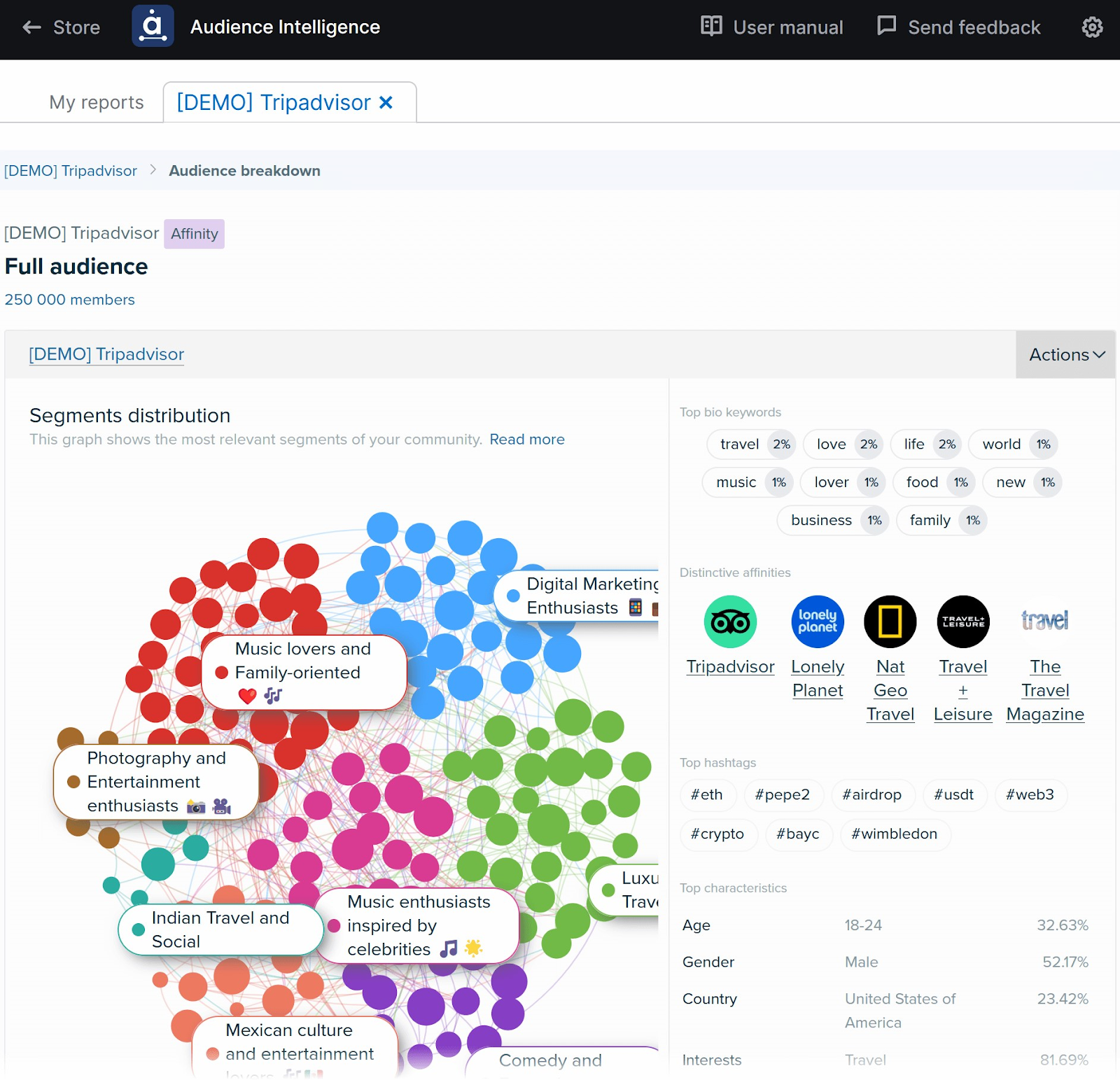
After you’ve learned about your competitors’ ads, leverage an audience intelligence tool.
It’ll help you get insights into your audience’s online behavior, personalize your messaging, identify top promotional channels, and more.
Create a free Semrush account to try AdClarity and Audience Intelligence.
