Want to make a page rank higher in Google?
This on-page SEO checklist is your ultimate companion.
On-page SEO is the process of optimizing individual page content to rank higher on Google. Activities include optimizing title tags and URL slugs, adding header tags, and much more.
Complete all 11 tasks (and three bonus tasks) in this checklist, in any order. To optimize your content for target keywords, make your page Google-friendly, and improve user engagement.
Here’s the complete on-page SEO checklist:
1. Identify target keywords
2. Optimize the title tag
3. Write your headline in an H1 tag
4. Write a meta description that boosts clicks
5. Check the URL slug for SEO-friendliness
6. Add target keywords to your body content
7. Review your content quality
8. Mark up subheadings with header tags
9. Improve navigation with internal links
10. Add engaging visual content
11. Apply schema markup
Bonus:
12. Make sure your page is indexed
13. Increase page speed
14. Make sure your page is mobile-friendly
Tip: Download this checklist and check the boxes as you complete each task.

1. Identify Target Keywords
Target keywords—i.e., relevant search queries—are crucial to on-page optimization. After all, the goal is to rank for relevant keywords and become more visible in search results.
Perform keyword research to find what words and phrases people use to find pages like yours.
Semrush’s Keyword Magic Tool is the biggest keyword database on the market. And it provides data you can use to choose the best keywords for your brand.
Those data points include:
- Intent: The type of search intent or motivation behind each search
- Volume: Keyword search volume, the average number of monthly searches
- KD%: Keyword difficulty, a measure of how hard it will be to rank in the top 10 unpaid Google results

Here’s what keyword research looks like in action:
Let’s say you owned a flower shop. The keyword “blue flowers” might seem like a great keyword to target.
But is it?
The keyword gets a lot of search interest—60,500 searches per month. But it also has a keyword difficulty of 63%. Which means it’s difficult to rank for.
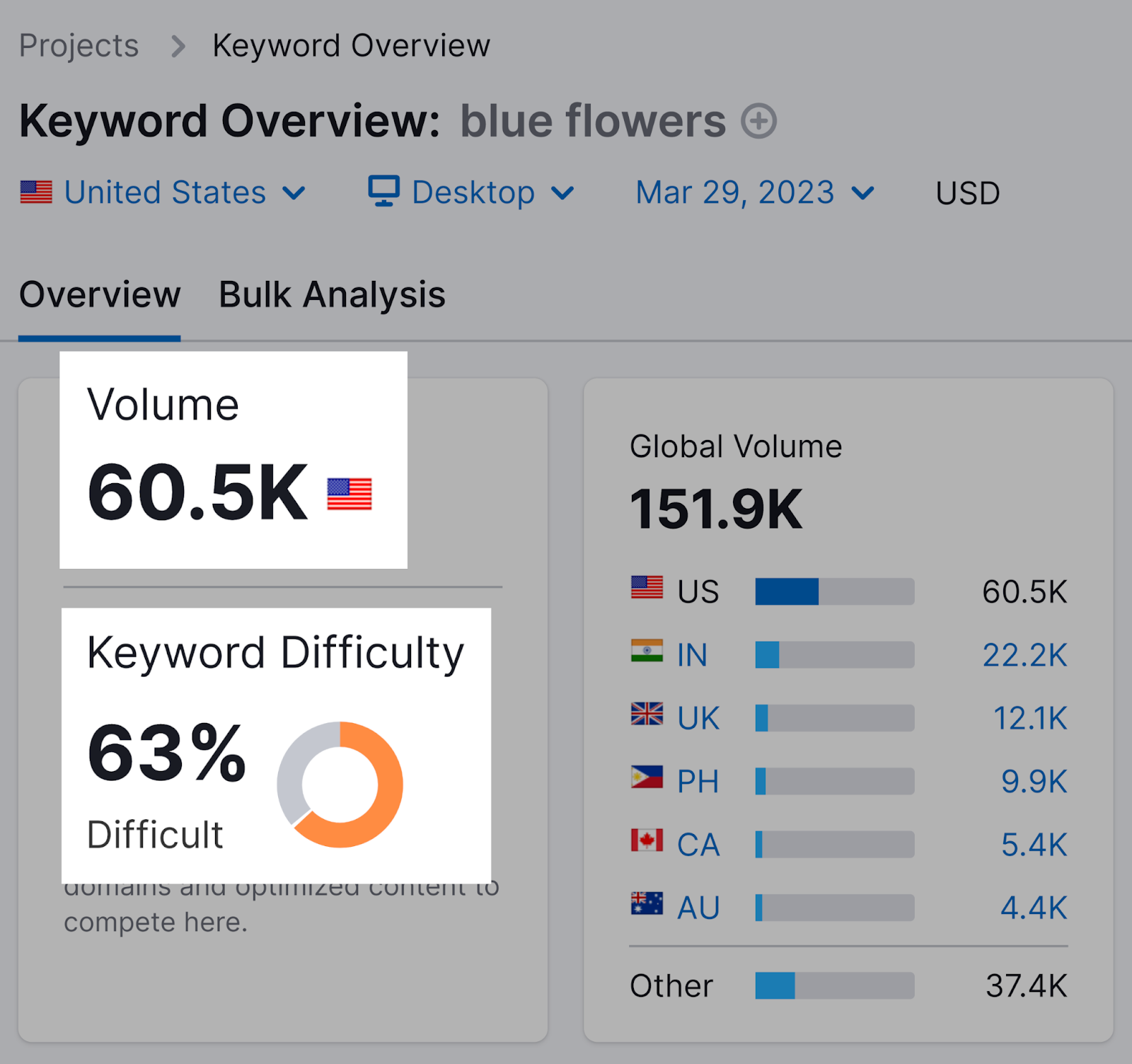
On top of all that, the search engine results page (SERP) is dominated by informational articles. Which means most searchers are looking to learn more about flowers—not make a purchase.

So if your goal is to increase sales, then “blue flowers” might not be the keyword for you.
You can identify the best target keywords by performing keyword research and understanding search intent. Then, you can optimize your page accordingly.
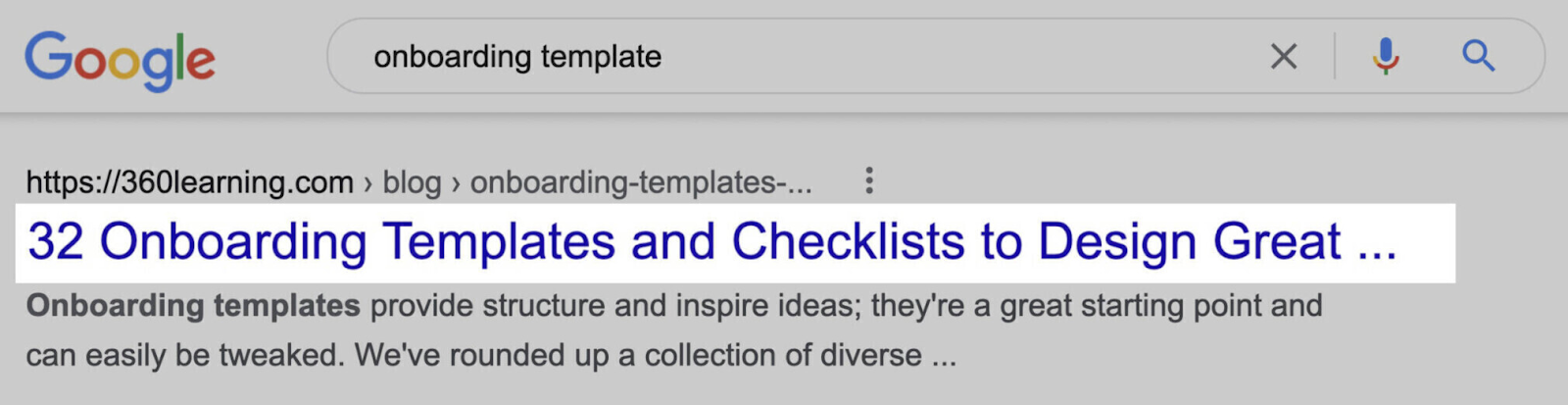
2. Optimize the Title Tag
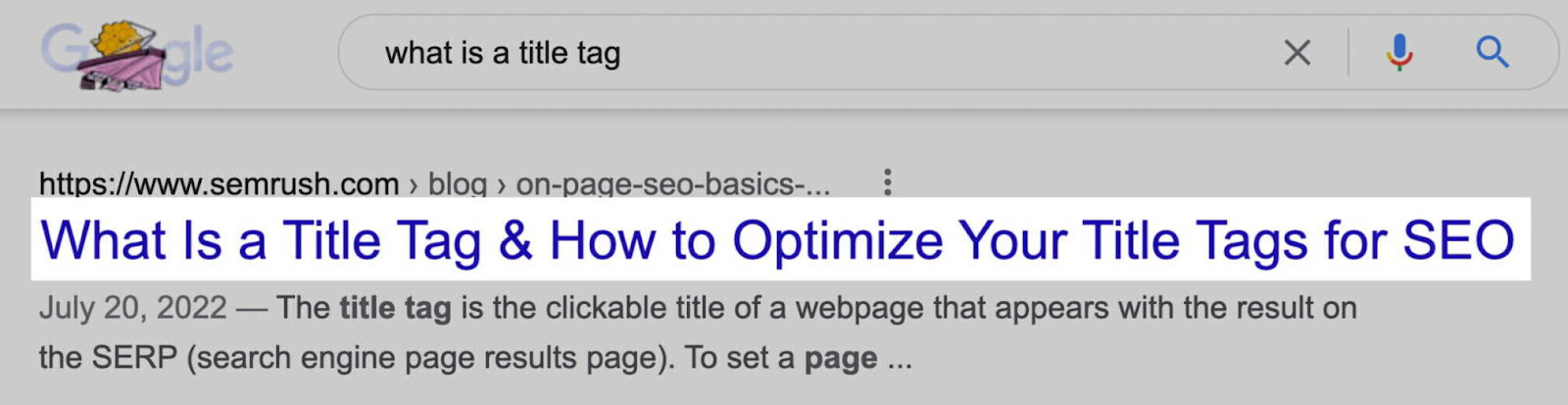
The title tag is the page title that appears in the SERP. It should tell Google what your page is about. And entice users to click through.
It looks like this on the SERP:
And this in the HTML code:
<title>What Is a Title Tag & How to Optimize Your Title Tags for SEO</title>The title tag is one of the most important elements for on-page optimization. So make sure to include the page’s primary keyword (the main search term you want to rank for). Ideally, at the start.
You can add secondary keywords, too. But it’s important to avoid unnatural “keyword stuffing.” This can look spammy to Google and users.
Tip: Semrush’s On Page SEO Checker checks your title tag for target keywords and keyword stuffing.
Open the tool and create your project.
After that, go to the “Optimization Ideas” tab. You’ll see your website pages and number of optimization ideas for them.
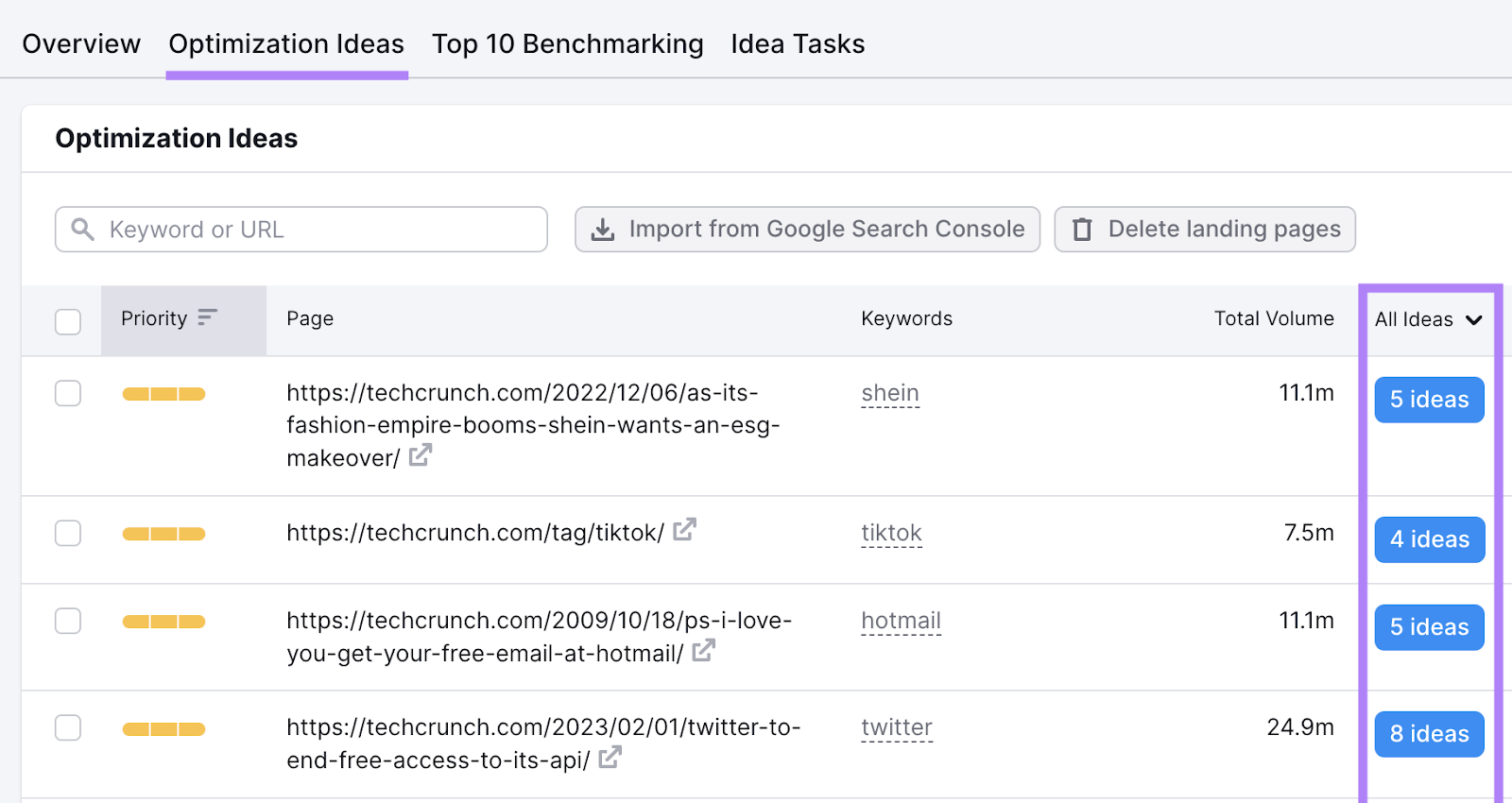
Click on “X ideas.” The content section will tell you whether your title tag includes target keywords without keyword stuffing.
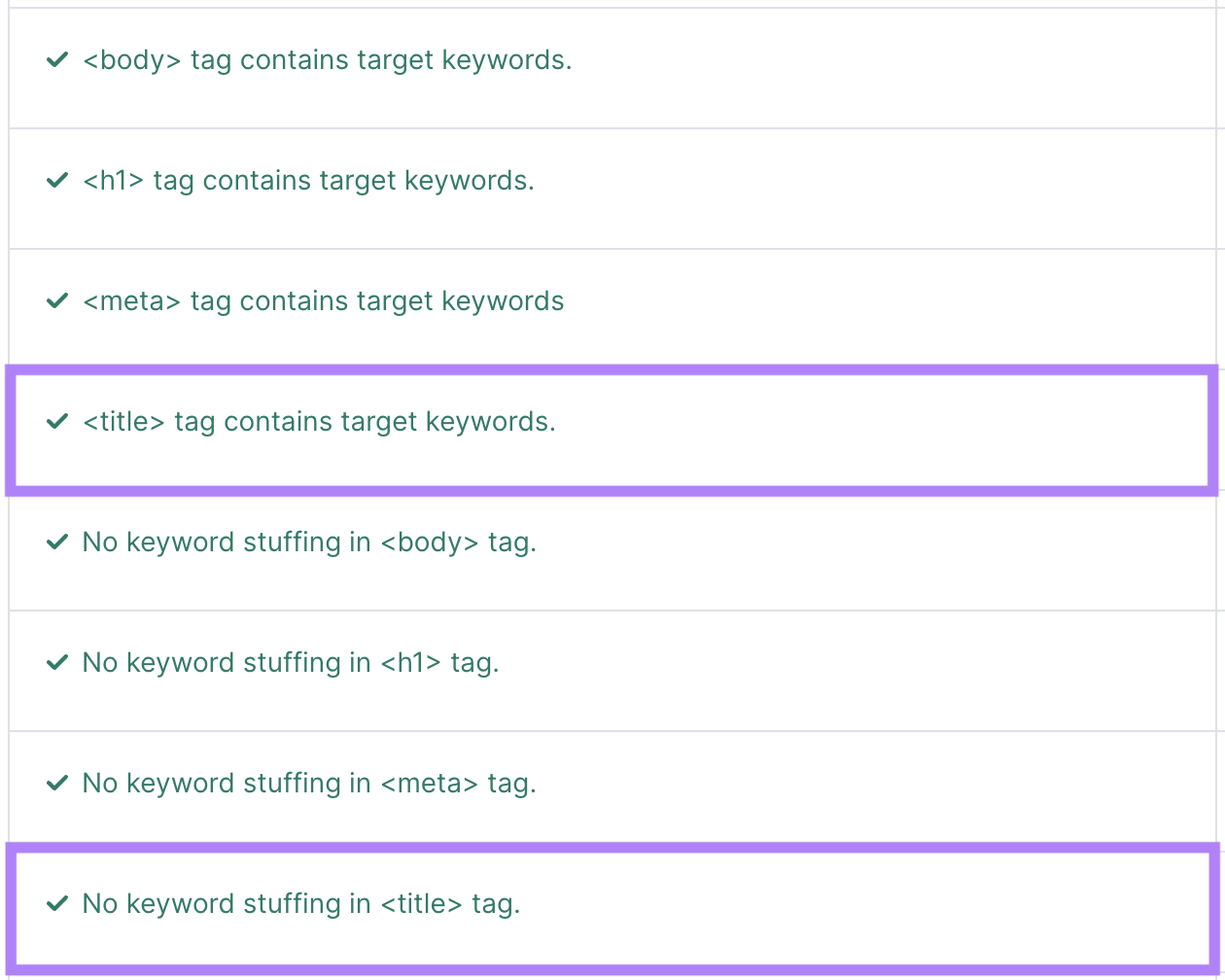
Also, aim for a title tag length of 50 to 60 characters (including spaces).
Because Google truncates title tags that are too long. Like this:
3. Write Your Headline in an H1 Tag
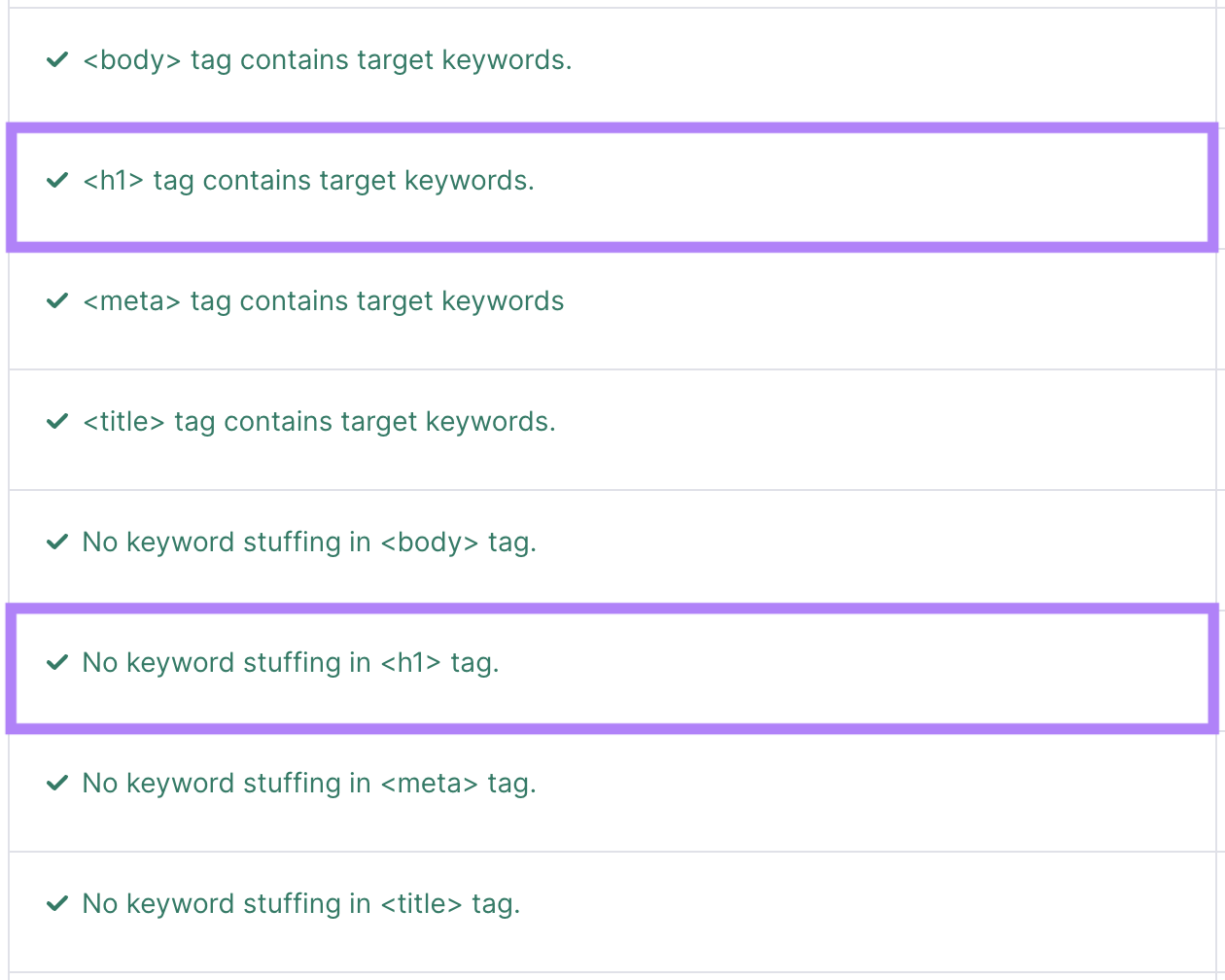
Every page should have one H1 tag that contains the on-page title (or headline). It’s one of the simplest yet important tasks in this on-page SEO checklist.
The H1 differs from a title tag because the H1 appears on your page. Not the SERP.
Here’s an example of what it looks like in HTML and on the page:

The H1 tag should be similar to the title tag. As it’s also there to tell Google and users what the page is about.
However, there’s rarely a character limit here. Just focus on creating an H1 that makes sense on your page and encourages visitors to stay. And include your primary keyword, at least.
Tip: Semrush’s On Page SEO Checker checks your H1 tag for target keywords and keyword stuffing.
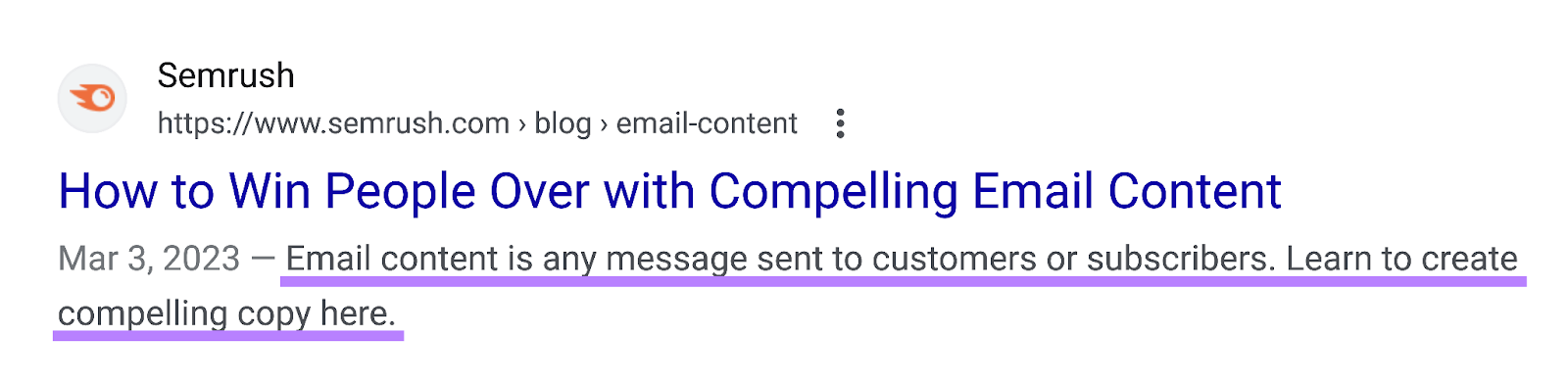
4. Write a Meta Description That Boosts Clicks
The meta description is the page description that appears in the SERP.
It looks like this on the SERP:
And this in your HTML code:
<meta name="description" content="Meta description here.">The meta description isn’t a direct ranking factor. It’s part of this on-page optimization checklist because it’s key to standing out on the SERP and attracting more clicks.
Use it to explain what the user will get from your page and why it’s worth visiting. And make sure it includes your primary keyword.
(Google often bolds users’ search queries in meta descriptions on the SERP. Making your listing potentially stand out more.)
Note: Google may generate its own title tags and meta descriptions for your pages. Optimizing them can reduce the risk of this happening.
We recommend sticking to a maximum of 120 characters (including spaces) for your meta descriptions. This reduces the risk of Google truncating them in desktop and mobile SERPs.
Tip: Semrush’s On Page SEO Checker will check your meta description for target keywords and keyword stuffing. It will also flag if Google is rewriting your description in the search results.

5. Check the URL Slug for SEO-Friendliness
The URL slug is the part of the URL that’s unique to the page.
In this example, the URL slug is “what-is-a-url-slug”:
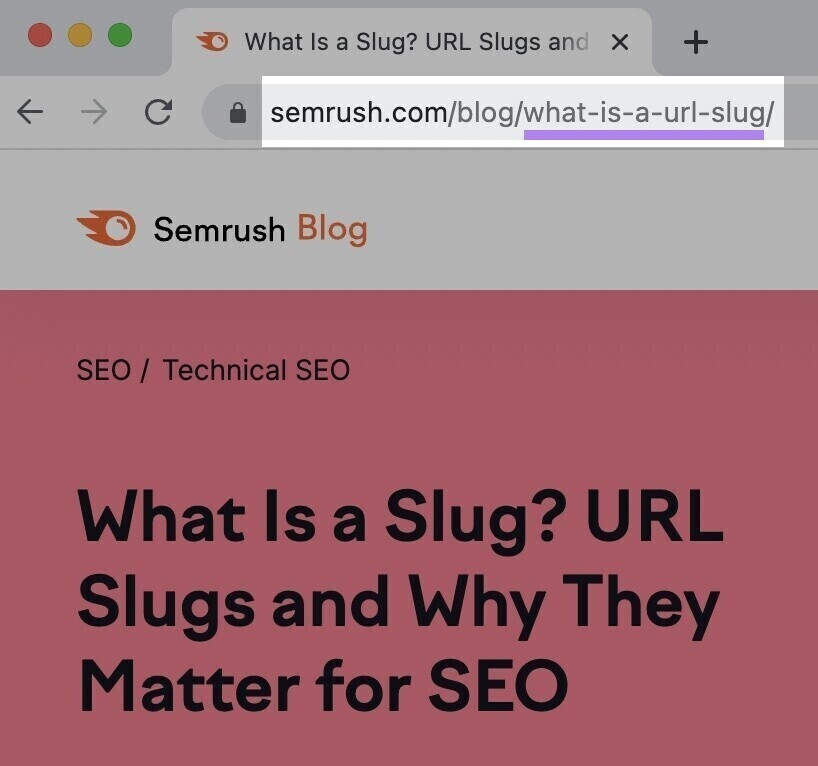
The URL slug should be concise, clear, and descriptive.
Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Consider using your page’s primary keyword as the URL slug
- Separate words using a hyphen (“-”)
- Avoid mentioning years that might change (e.g., “best-headphones-2023”)
- If you change your URL slug, make sure to redirect the old version
Check out our dedicated guide for more advice on creating SEO-friendly URLs.
6. Add Target Keywords to Your Body Content
Google uses keywords and context to determine whether a page is relevant to a specific keyword. If your body content doesn’t mention your target keyword, Google may think your page is not relevant to the keyword.
When doing on-page optimization, use your primary keyword within the first paragraph. And then scatter repeats (and/or secondary keywords) throughout.
But avoid keyword stuffing—i.e., forcing keywords where they don’t sound natural.
Here’s an example of keyword stuffing from Google:

Remember that you’re writing for users. Not just search engines.
Look at the top-ranking pages to see what’s working well for them.
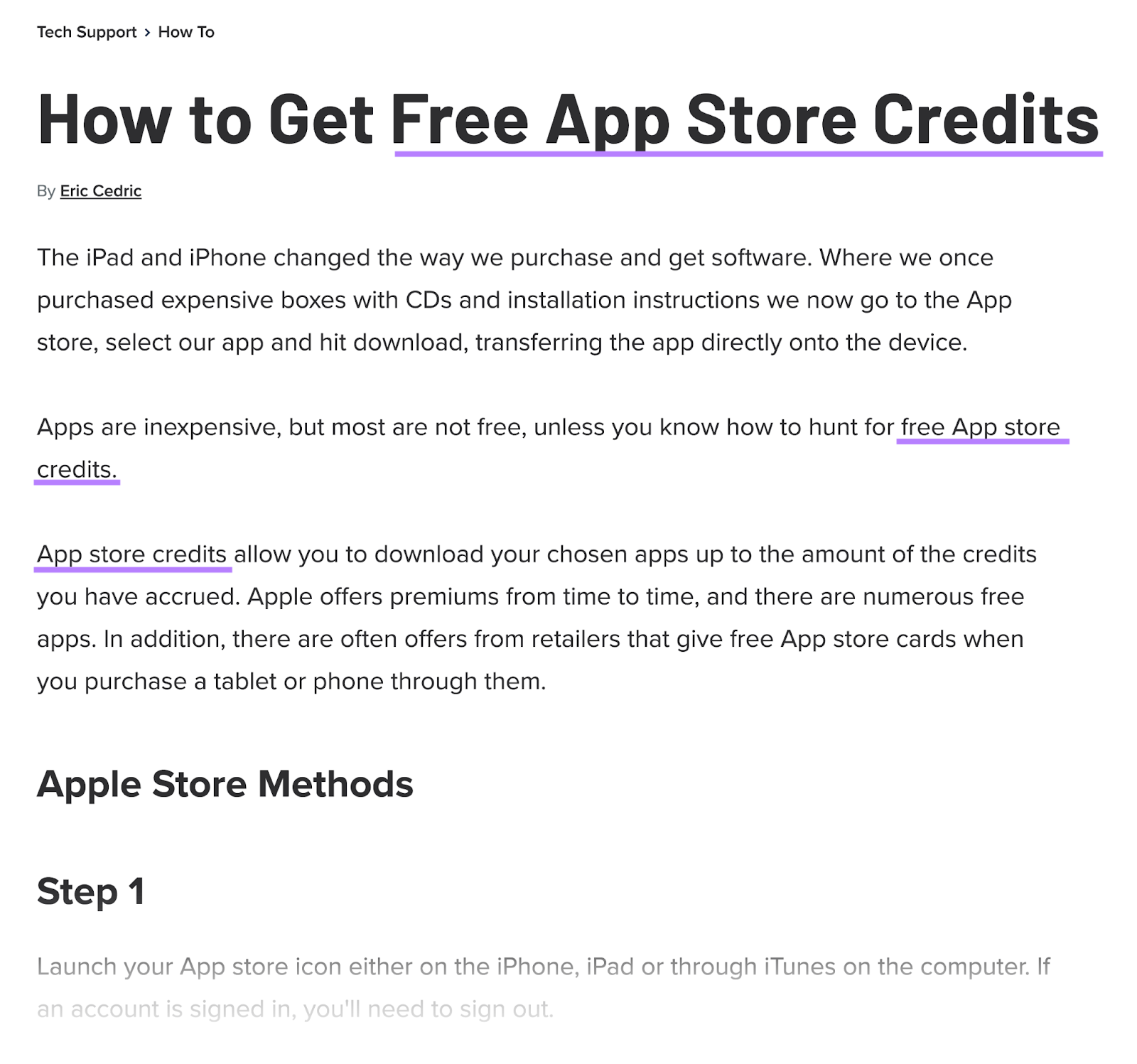
Or save time with Semrush’s SEO Content Template. It provides key recommendations based on the top 10 results for your target keyword(s).
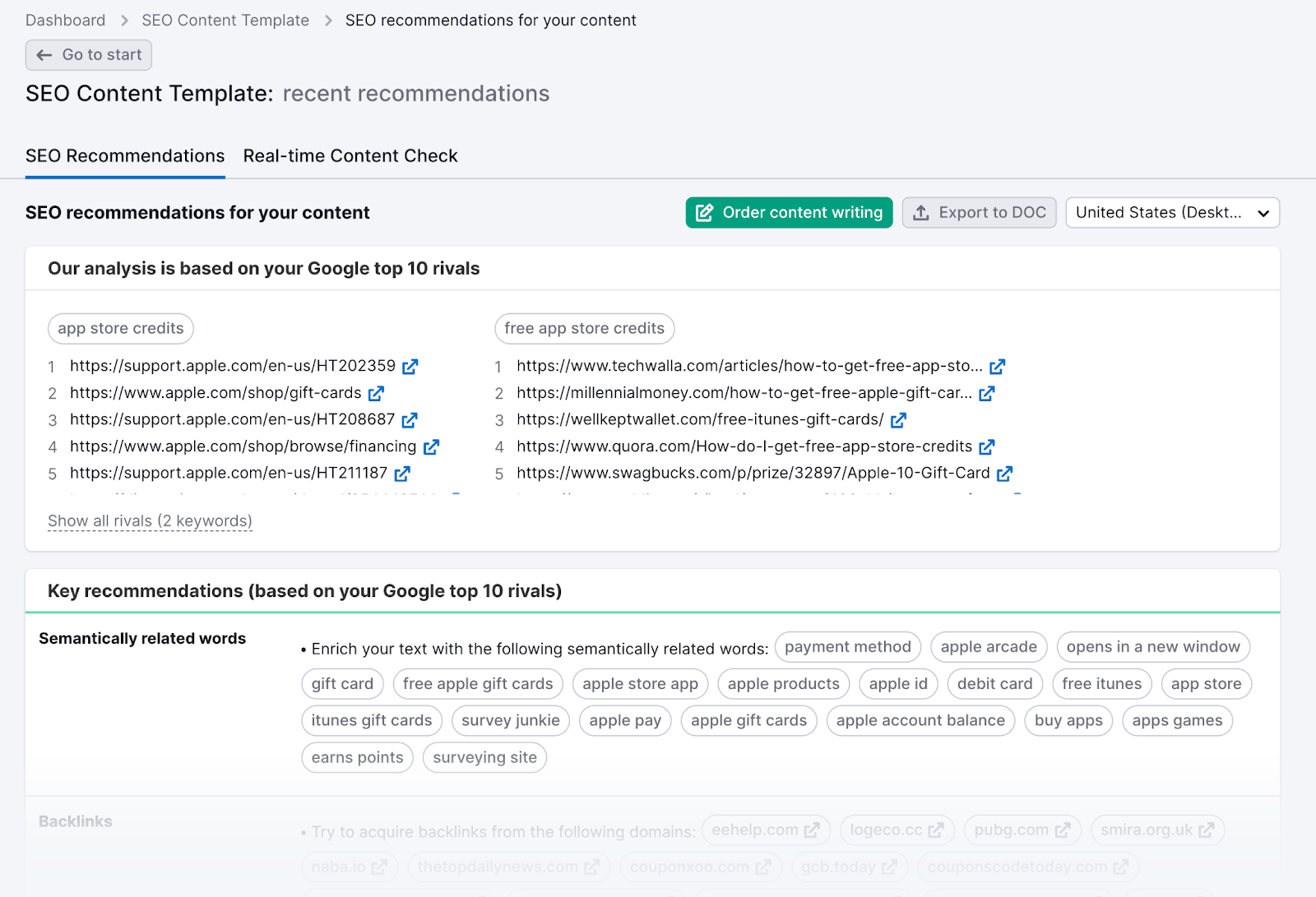
And makes it easy to analyze your rivals’ keyword usage.
7. Review Your Content Quality
The nature of your content largely depends on search intent. For example, a short description might satisfy someone shopping for products. But someone seeking information might want an in-depth guide.
Either way, your content must meet high standards to compete on the SERP and keep users engaged. That’s why you need to review content quality when completing your on-page SEO checklist.
Here are some of the main content quality indicators:
| Quality indicator | Best practice |
| Accuracy | Content should be factually correct and up to date. It should also be free of spelling and grammatical errors. |
| Originality | Avoid duplicating large chunks of content across your site. Also ensure there are no instances of plagiarism (copying of content from elsewhere). |
| Length | Concise content is more engaging. But be comprehensive—provide all the information the searcher needs at this stage. |
| Readability | Readers are more likely to exit your page if your writing is too hard to read—or too simplistic. Make sure the reading level is appropriate for your audience. |
| Formatting | Paragraph breaks, subheadings, tables, bullet points, and other formatting elements can make your text more engaging. |
| Tone of voice | It’s not just what you say but how you say it. The right tone of voice depends on your subject matter and target audience. |
Run your content through Semrush’s SEO Writing Assistant and make improvements there.
The tool provides SEO, readability, and tone of voice suggestions based on the top 10 competitors for your target keyword(s). And checks for plagiarism.

If you get writer’s block, you can use the built-in AI to compose or rephrase content.
8. Mark Up Subheadings with Header Tags
Semrush’s State of Content Marketing Report 2023 found that 29% of high-performance articles use H2, H3, and H4 tags.
That’s because subheadings break up text and make it easier for users to scan your content. And the appropriate H-tags (header tags) help Google understand the structure of your page.
You should only have one H1 header. But you can add as many H2 through H6 tags as necessary, depending on the depth of your content.
They work in a nested hierarchy system. Like this:

Tip: Where natural, include secondary keywords in your header tags.
9. Improve Navigation with Internal Links
Internal links are links between pages on your site. They help Google and users to find their way around.
For example, Soak&Sleep has internal links to its “single duvets” and “single mattresses” categories in its “single bedding” page description.
(There are also helpful links in the navigation menu, breadcrumb navigation, and other elements.)
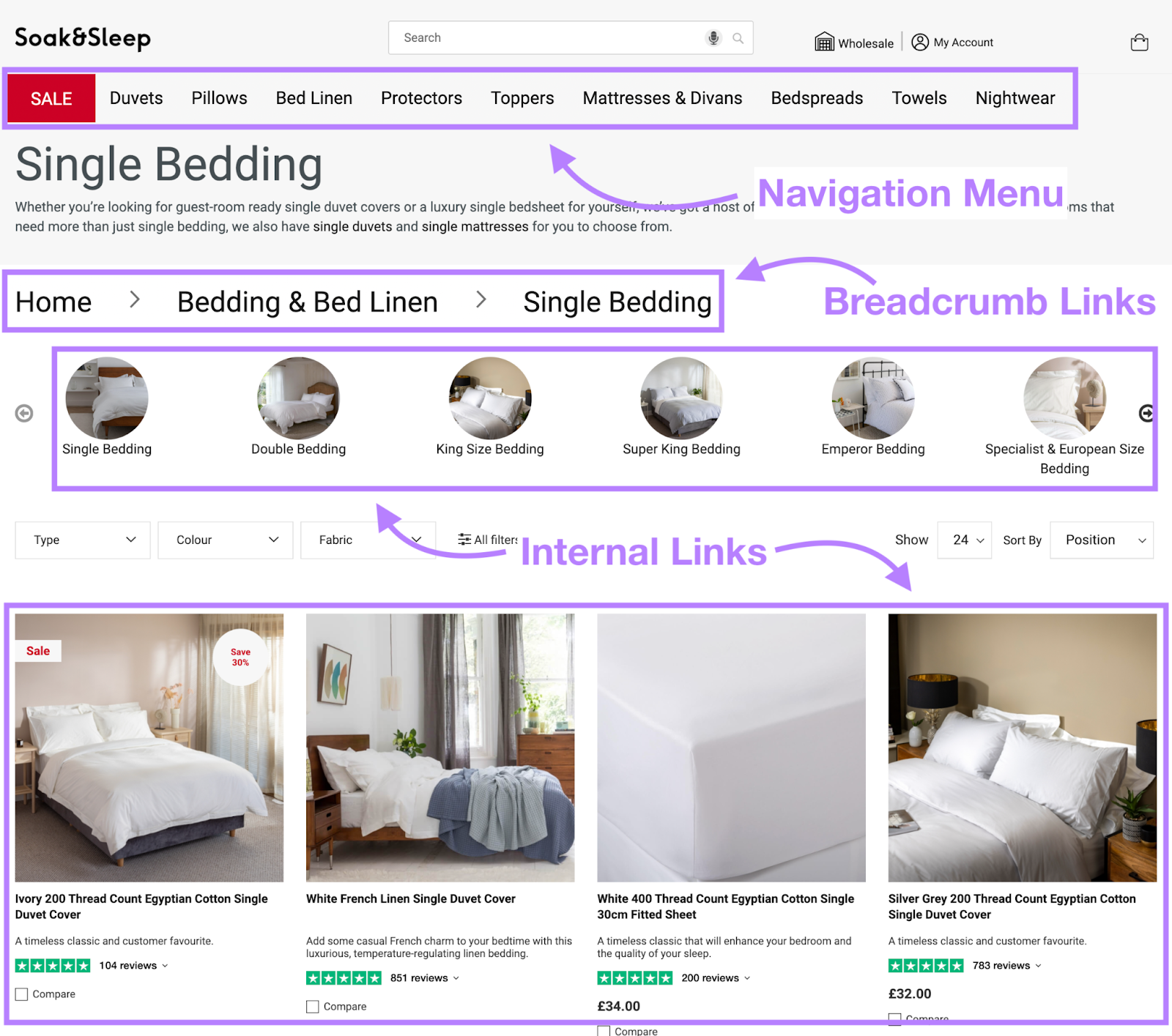
Notice how these internal links are attached to descriptive anchor text—not generic text like “Click here.” This helps Google (and users) understand what the linked page is about.
Tip: Working on informational pages? Consider adding external links to your on-page optimization checklist as well. Linking out to high-quality resources indicates that you’ve done your research and have readers’ best interests in mind.
10. Add Engaging Visual Content
Use images and videos wherever they add value to your content. This includes photos, illustrations, how-to videos, and more.
Articles with more images tend to get more unique page views, shares, and backlinks, Semrush research shows.
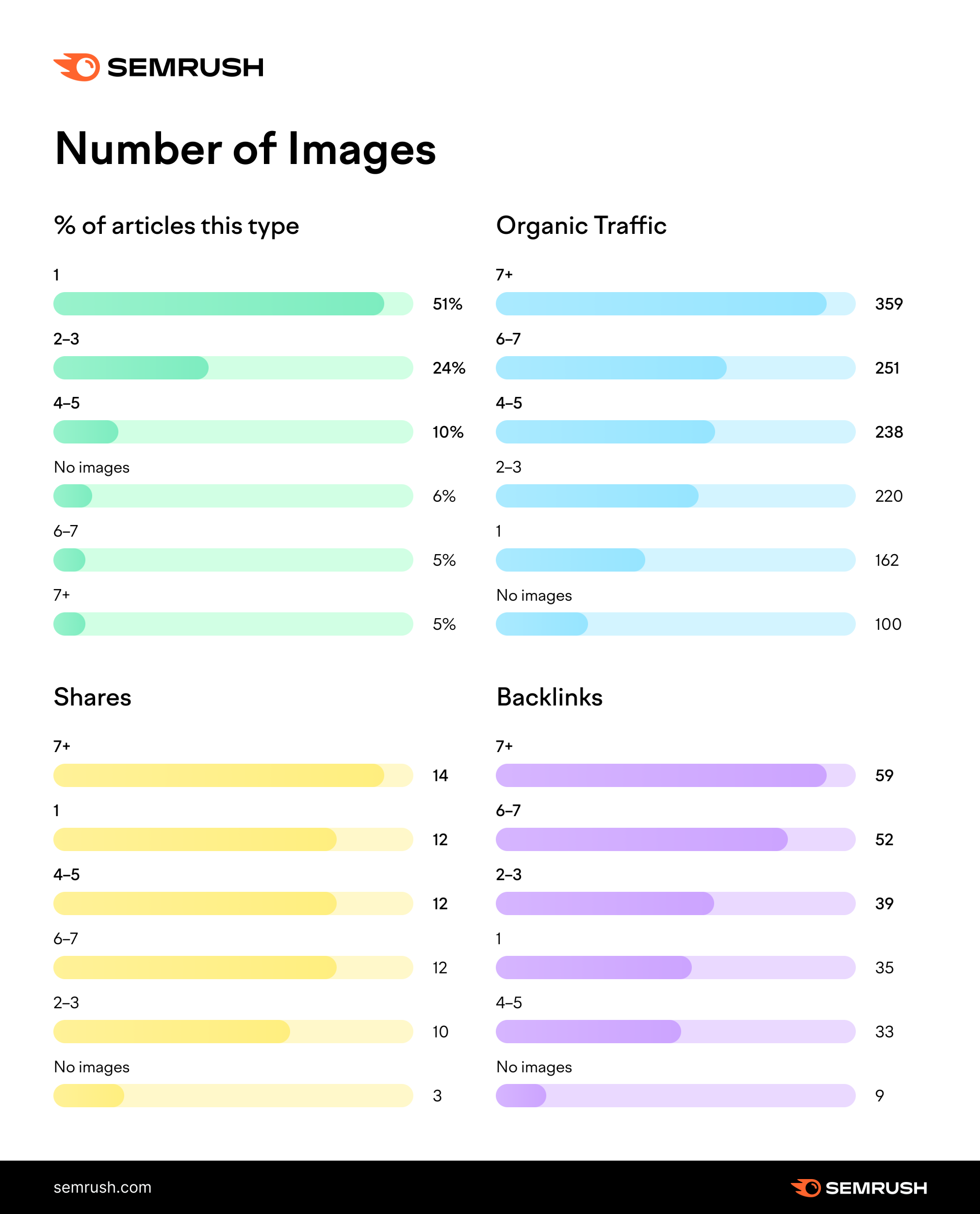
And articles with videos get more unique page views, shares, and backlinks.
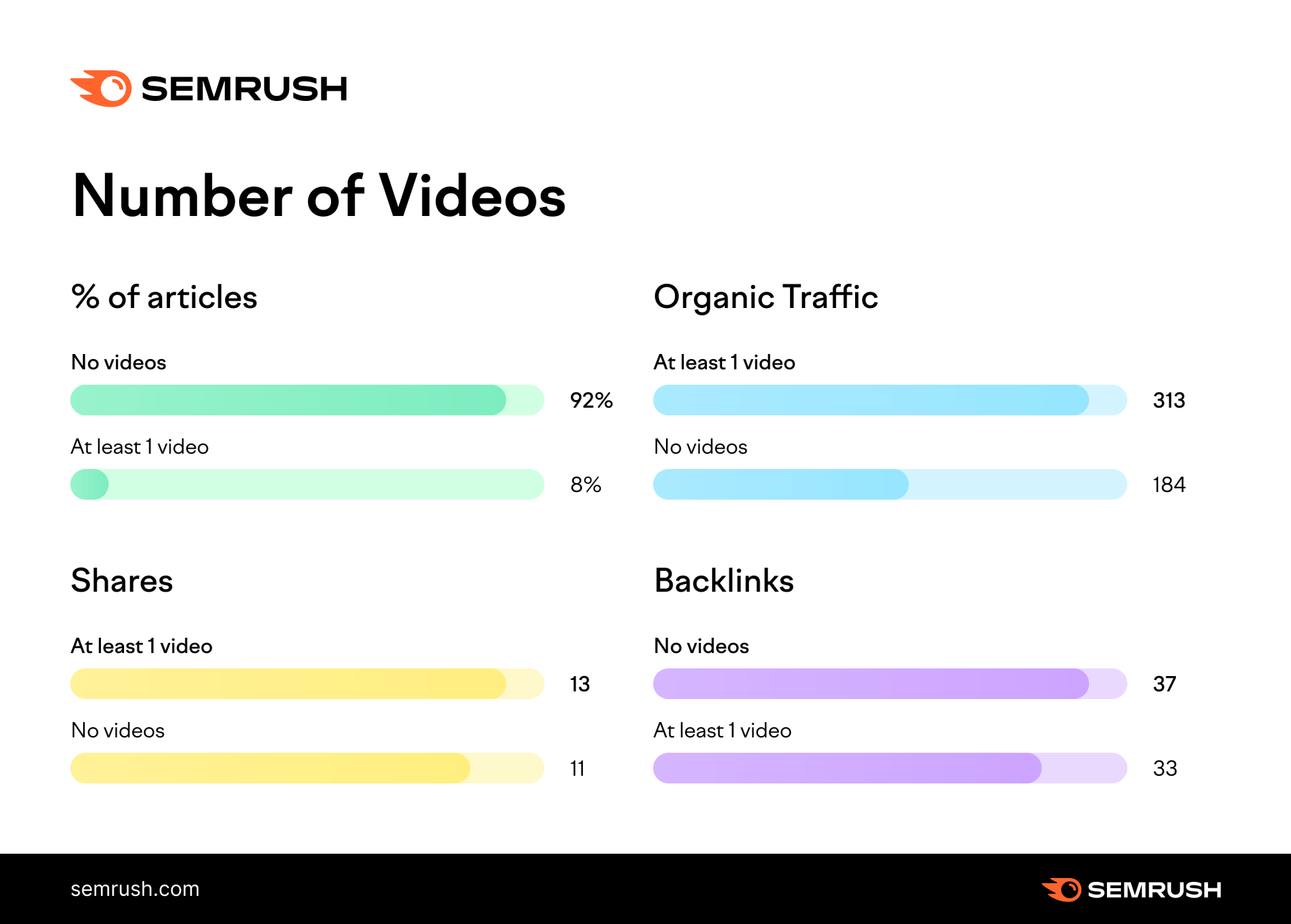
Which is why you should use them to break up the text where appropriate.
Here are some tips when adding images:
- Add descriptive alt text to each image. This is a written image description that appears in the page’s code.
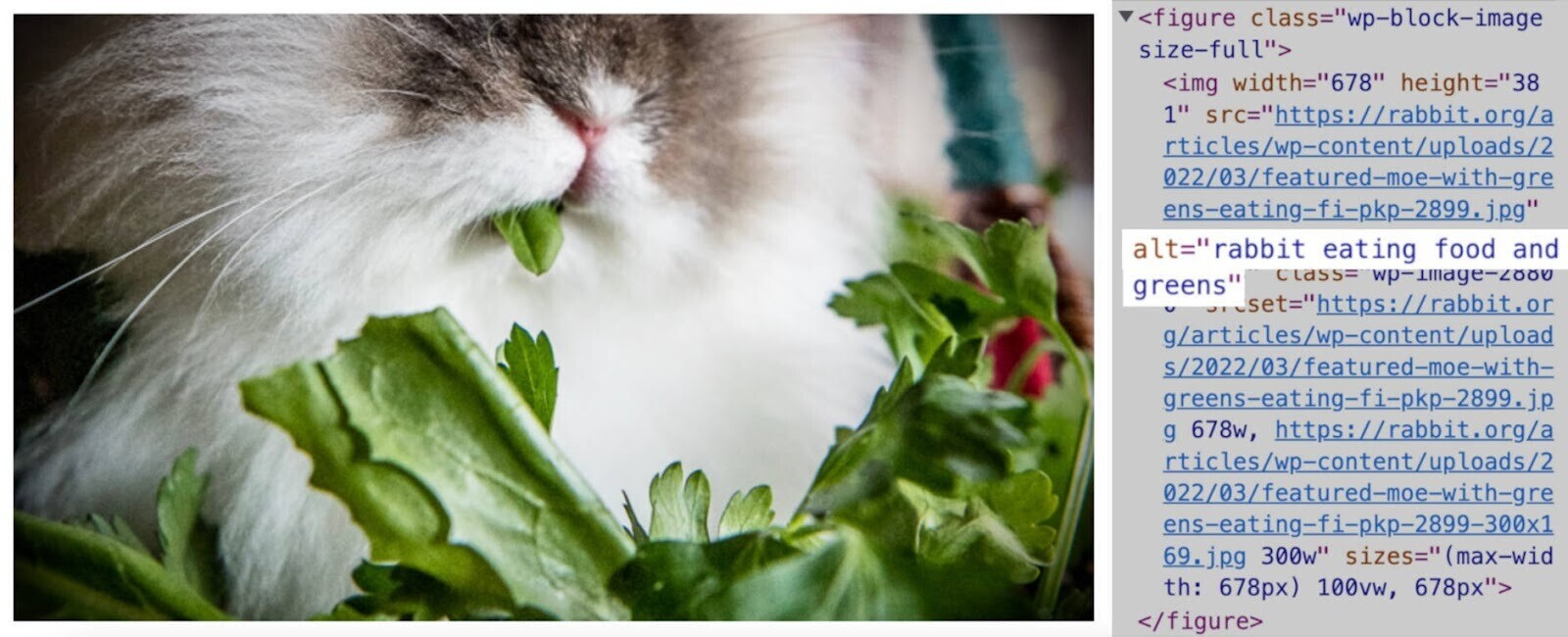

- Resize and compress your images with tools like BIRME. That way, your images don’t slow down your page loading time.
And here are some tips for using videos:
- Create videos that match search intent. For example, create tutorial videos to support your written how-to guides.
- Host your videos on YouTube—one of the largest search engines on the internet. And embed your videos from there.
Learn more about image SEO and video SEO with our in-depth guides.
11. Apply Schema Markup
Schema markup or structured data is a coding language that “tells” Google more about the different types of data on your site. And the better Google understands your page, the more accurately it can rank your content.
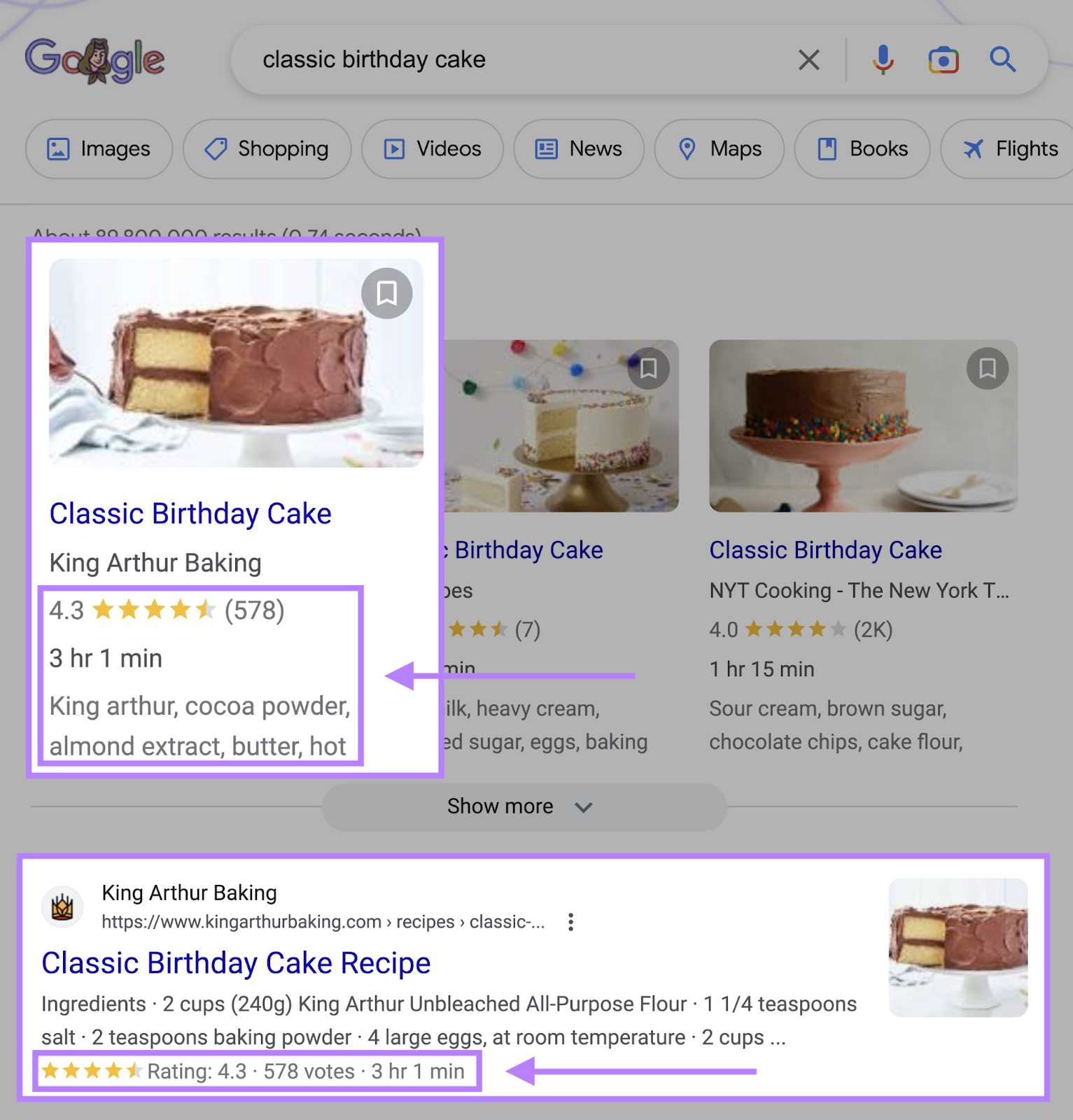
Google also uses these pieces of code to create rich results (or “rich snippets”).
For example, “Recipe” schema helps King Arthur Baking earn a valuable spot on the SERP. And gives users more information about the page’s content—ratings, time to make, and ingredients.
Google supports 32 types of schema. Including Article, Event, FAQ, How-to, Product, and Local Business schema.
This is one of the more advanced tasks on this on-page SEO checklist. But Google does have a Structured Data Markup Helper that helps you add schema to your page.
Learn more in our guide to schema and structured data.
BONUS: Start on Your Technical SEO
While technical SEO is different from on-page SEO, you need both to rank well on Google.
Read our in-depth guide to technical SEO. But here’s a brief overview to get you started.
1. Make Sure Your Page Is Indexed
For your page to appear in search results, Google’s web crawlers must first add it to the Google index.
You can check if your page is indexed via Google Search Console.
Tip: Haven’t used the tool before? Our Google Search Console guide will help you get set up.
Just inspect the page’s URL using the search bar. Then look at the information provided.
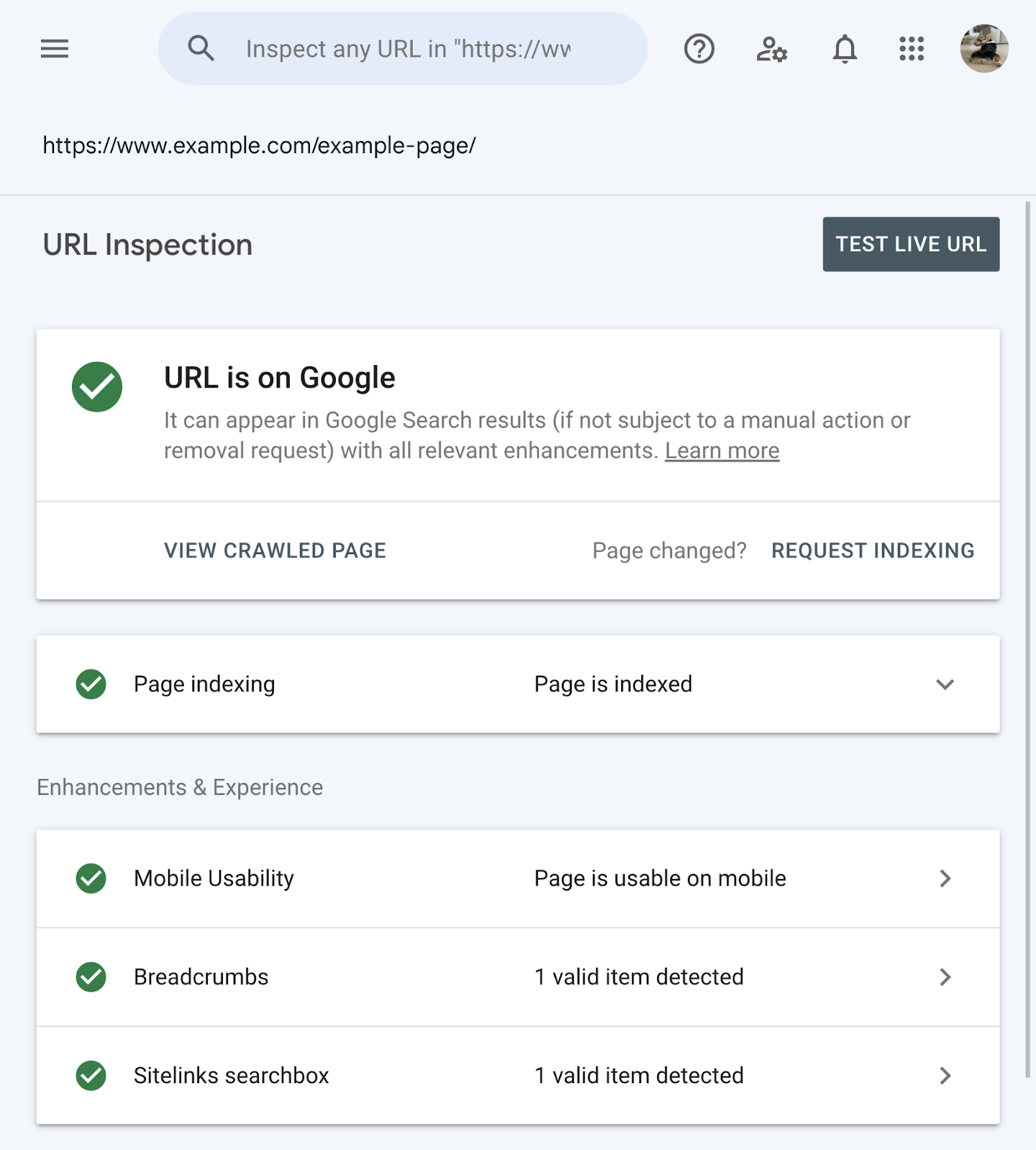
If your URL is not indexed, check out our guide to Google indexing.
Alternatively, use Semrush’s Site Audit tool to find all crawlability issues on your site. Simply click on the “Category” filter and select “Crawlability” to get a list of issues.
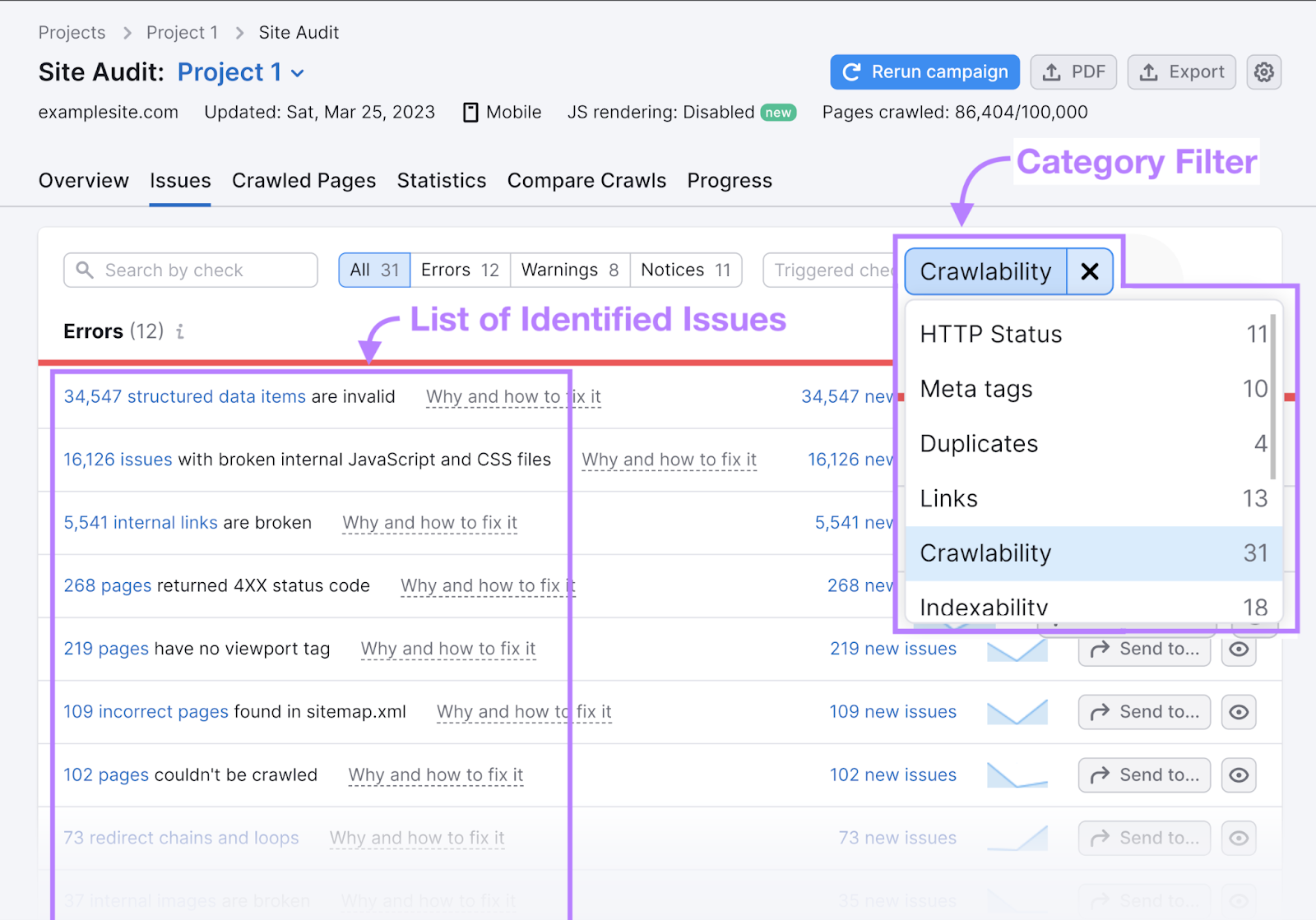
The tool provides suggestions on how you can fix them.

Or take a look at the Crawlability report in Site Audit.
2. Increase Page Speed
Google and users want pages that load quickly. The smallest delay can drive visitors to close your page and go elsewhere.
Here’s a quick list of things that could slow down your page speed:
- Large amounts of HTML on the page
- Redirect chains
- Large JavaScript or CSS files
Check your page speed in Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool. Just enter your page’s URL. Then click “Analyze.”
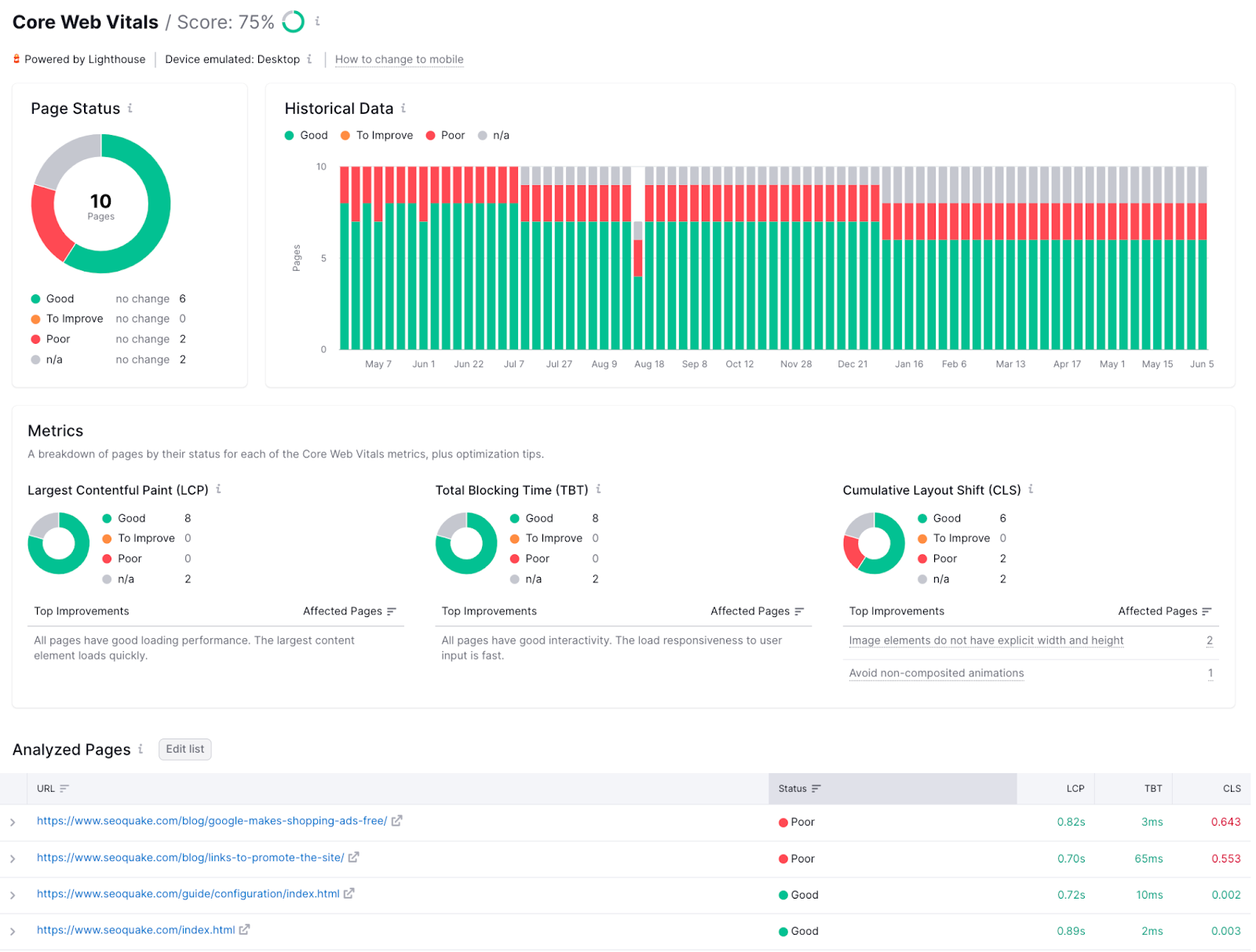
Then look at your “Core Web Vitals Assessment” (on “Mobile” and “Desktop”) to see whether you passed. Core Web Vitals are key speed metrics that affect user experience. And Google rankings.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): The time it takes for the main content of the page to appear
- First Input Delay (FID): The response time to the user’s first interaction
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): A measure of layout movements that occur during loading

Semrush’s Site Audit tool has a Core Web Vitals report that analyzes up to 10 pages per crawl.
3. Make Sure Your Page Is Mobile-Friendly
More than 60% of Google searches are performed on mobile devices. So Google predominantly looks at the mobile version of a page when evaluating its quality (and determining its rankings).
This means mobile SEO is paramount.
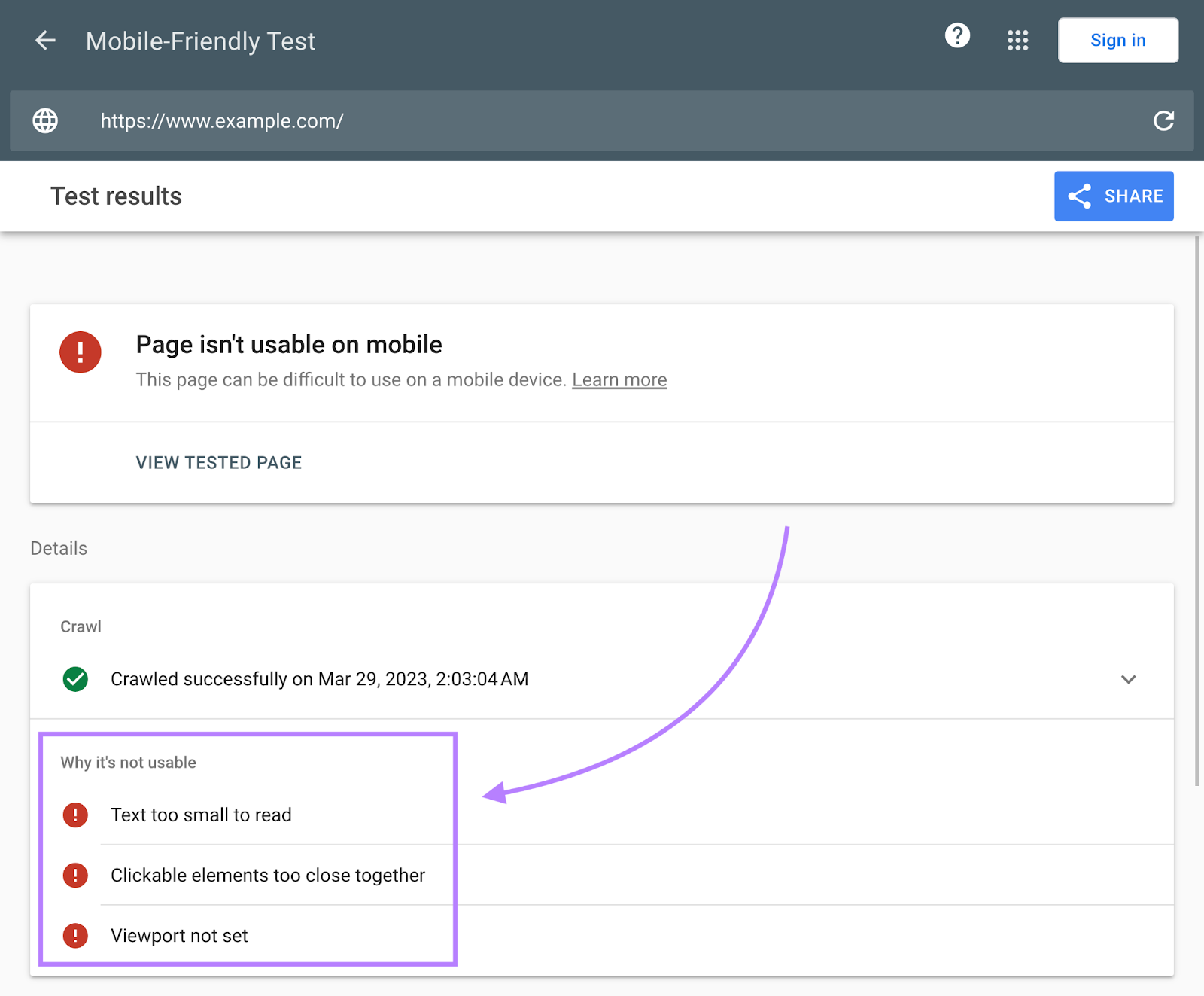
Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to find out if your page delivers a good user experience on mobile.
Just enter your page’s URL. Then click “TEST URL.”
If your page “isn’t usable on mobile,” look at the “Why it’s not usable” section. And click a problem to get more details.
Improving mobile-friendliness isn’t necessarily something you can do in a day. (Unlike many of the tasks in this on-page SEO checklist.) But it’s usually worth the time investment.
Create Your Own On-Page SEO Checklist
Use this free template to create your own interactive on-page SEO checklist. It’s the best way to track your progress as you complete each task for each page.
And don’t forget to take advantage of the on-page optimization tools available with Semrush. You can access our On Page SEO Checker and much more with a free account.
Looking for more ways to increase organic traffic? See our SEO checklist for a full breakdown.
